Interviews, Speeches, Books and Writings
In this catalog, we invite you to explore Justice O'Connor's speeches, interviews, and writing throughout her career.
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. And that was the best introduction I’ve ever had. From the best sister I’ve ever had. I can’t tell you how pleased I am to be here with you today to commemorate the ratification of the 19th amendment. We’re starting this talk a little early. Maybe before you’re finished with launch, and we’re doing that because I have so much to tell you today. I normally try to be very brief in my speeches. I’m not going to be brief today. Because this is a story that needs telling and you need to know what if you don’t Ready.
I find it difficult to imagine that only 75 years ago, a woman’s right to vote was not protected by our Constitution. It’s hard to remember that we have taken for granted all our lives, something that some of our grandmothers never enjoy. But we’re here today to remember such things, to celebrate the amendments that extended to women, one of the fundamental rights of citizen participation, and to reflect on how far we’ve come. In order to appreciate the tremendous progress made by American women in the last century. It’s important to think about the point from which we started the history of the suffrage movement. He has a colorful and entertaining one and a tale from which we can draw many lessons. begins in the late 18th century, as this country’s political, governmental and social frameworks were only beginning to take shape. When the wife of future president john adams implored her husband in 1776 to remember the ladies and drafting
Acceptance speech for award from Congressional Families Action for Cancer
Host Herself a cancer survivor, Mrs. O’Connor has made advocating unified team treatments for cancer patients for special cause. From her vantage point on the world’s most noticed, and most influential judicial panel, she can not only see what the public’s needs are, but with one word can greatly influence outcomes. Her advocacy of early detection and treatment weighs greatly with the American public. And we salute her efforts with this award today, for she i think is probably the best example in the world, that having breast cancer is not a death sentence, but that you can go on and be anything you want to be if you just address the problem. We honor you today. And please join me ask everyone here to join me in giving her our award today. Thank Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. Thank you. I must say, Debbie, it was lovely to hear those words. But when I hear about the others you’ve honored today and hear the work that Dr. Klausner and people like Dr. Klausner are doing, I feel that my contribution to this discussion has been very small indeed. What this organization is about is building bridges, building bridges, from your communities and the wide sphere of brands and influence that each of you have to the centers of knowledge and skill and understanding about cancer and prostate cancer and what can be done to alleviate them? So your bridge builders and the other honorees or bridge builders, my bridge is very small. But my honor is very great. And being here today and being with
The Life of the Law: Principles of Logic and Experience from the United States
ADDRESS
THE LIFE OF THE LAW: PRINCIPLES OF LOGIC AND EXPERIENCE
FROM THE UNITED STATES THE FAIRCHILD LECTURE*
THE HONORABLE SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR..
These are times of tremendous change in governments across the world. Since the mid-1980s, a remarkable number of countries in Latin America, Africa, and the Soviet bloc have turned from dictatorship to elected civilian government. In several visits to Eastern Europe, I have been impressed by the strides taken by these countries toward their goals of liberty and democracy. But if they are to retain and build on their recent gains, the new governments must put into place a framework that can ensure the survival of basic freedoms. Of course, such a framework must be adapted to the political and cultural history of each country. Already, we see the post-communist countries begin to differ significantly in their political, constitutional, and social development. Despite the important differences among nations, and forms of governments, however, some basic principles must be enforced if a government is to ensure the liberty of its citizens.
Since emerging from the grip of the Soviet Union, developing nations of Eastern Europe have looked to Western ideas about economic structure, the relationship among branches of government, and the relationship of the individual to the community for guidance in designing their own institutions and processes. Tonight I would like to discuss certain aspects of our governmental scheme that have been
In Memoriam: A Tribute to Warren E. Burger
A TRIBUTE TO WARREN E. BURGER
The Honorable Sandra Day O’Connor*
A Chief Justice is always a special figure in American history, and indeed, only sixteen Justices have held that position since our Constitution was ratified. Warren E. Burger was the fifteenth Chief Justice, and his seventeen years in that capacity were distinguished by his energy and his efforts to improve the judicial system throughout the United States. His life and his service as Chief Justice have left their imprint on many aspects of our legal system.
Chief Justice Burger graduated magna cum laude in 1931 from Saint Paul College of Law, the earliest forerunner of William Mitchell College of Law. He was the president of his law school fraternity, Phi Beta Gamma, which, in uncanny foresight, conferred upon him the title of “Chief Justice.” Warren Burger could not have attended a traditional day law school. He had married and started a family and found it necessary to hold a full-time job in the insurance industry to support his family. If it were not for the opportunity that Saint Paul offered him to attend law school classes at night, he would have been unable to enter the legal profession.
Throughout his career, Chief Justice Burger had a profound interest in raising the quality of the work of the judicial branch by improving the management of the courts. As Chief Justice, he worked to make the Supreme Court-and all courts-more responsive to the needs of those who used them. He left a legacy to the most
Religious Freedom: America’s Quest for Principles
It is an honour and a great pleasure to be standing here today in Belfast to deliver the MacDermott Lecture. In the inaugural lecture in 1972, Lord MacDermott suggested that the lectures be used to examine “our principal legal concepts” insofar as they impact on the “progress and happiness” of our communities. 1 My topic today is one that is central to the harmony and happiness of pluralistic western democracies, and one that, in very different forms, is a recurring concern in both Northern Ireland and America: religious freedom.
I shall focus on that with which I have some experience: the jurisprudence of the First Amendment to the US Constitution. In doing so, I make no pretence that American solutions can be imported lock, stock and barrel into other nations with quite different cultures, traditi_ons, and diverse religious groups. And I certainly do not claim to have a solution for this country’s problems of sectarian rivalry and conflict. But an American illustration of some key general features of a regime of religious freedom may, perhaps, stimulate thought and dialogue about what should be a goal shared by diverse religious and non-religious groups.
• • • • •
There is, as Justice Holmes once icily remarked, something “perfectly logical” about attempting to use the power of government to promote and impose upon others one’s own opinions. As Holmes explained, “if you have no doubt of your premises or your power and want a certain result with all your heart you naturally
Commentary (Organization of Justice in the Twenty-First Century)
COMMENTARY
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR*
It is a real pleasure to be here with you and to see this remarkable gathering of representatives of the highest courts of so many countries in this hemisphere. It is a wonderful step that you are taking, and one that I am sure will be helpful to all the participating countries in the future.
Justice Calvete gave a very thoughtful and insightful paper. He is to be commended for his presentation and the thought that went into it. He pointed out for us some of the far-reaching implications of trends that appear certain to affect the administration of justice far into the next century, which is right around the comer. Courts everywhere, not just in this hemisphere, are seeing increased caseloads. They are seeing increased caseloads in large measure because they are seeing increased populations-more people to serve, more cases to decide.
How do we predict what is going to happen in the future? How do we know? And what should we do about it? It seems to me that each country is going to have to make some long-range plans to deal with the problem. It is one thing to recognize it, but we have to plan to deal with it. Justice Calvete pointed to population growth and that is certainly correct. Demographers have a pretty good track record in the United States of plotting prospective changes in population. It is pretty clear in our country that as we go into the next century weare going to have many more senior citizens. People are living longer in our
Lessons from the Third Sovereign: Indian Tribal Courts
Today, in the United States, we have three types of sovereign entities-the Federal government, the States, and the Indian tribes. Each of the three sovereigns has its own judicial system, and each plays an important role in the ad ministration of justice in this country. The part played by the tribal courts is expanding. As of 1992, there were about 170 tribal courts, with jurisdiction encompassing a total of perhaps one million Americans.
Most of the tribal courts that exist today date from the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934.1 Before the Act, tribal judicial systems were based around the Courts of Indian Offenses, which were established in the 1880’s by the federal Office of Indian Affairs. Passage of the Indian Reorganization Act allowed the tribes to organize their governments, by drafting their own constitutions, adopting their own laws through tribal councils, and setting up their own court systems. By that time, however, enormous disruptions in customary Native American life had been wrought by factors such as forced migration, settlement on the reservations, the allotment system, and the imposition of unfamiliar Anglo American institutions. Consequently, in 1934, most tribes had only a dim memory of traditional dispute resolution systems, and were not in a position to recreate historical forms of justice. Swift replacement of the current systems by
* These remarks were delivered at the Indian Sovereignty Symposium IX in Tulsa, Oklahoma, on June 4, 1996. They are published
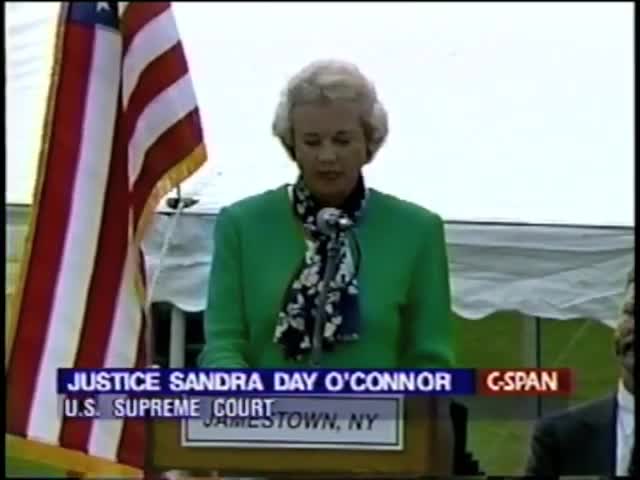
Speech at dedication of statue to the memory of Justice Robert H. Jackson
Sandra Day O’Connor This is a wonderful occasion for Jamestown and for all of us who are lucky enough to be here and see the unveiling of this absolutely handsome and strong statue of Justice Jackson. We’re remembering today a product of this community and of its public schools. The most treasured honor that anyone can receive is one that comes from one’s own town, from those who knew the honorary first and best, so it is today, Robert Jackson, one of the finest justices ever to sit on the bench of the United States Supreme Court, grew up on a farm close to Jamestown. It was here that he attended the Jamestown elementary and high school that he married, had his children and practice law. It was here that he spoke in 1935. At the dedication of the new Jamestown high school building, he said them. If you believe as I believe that democracy is the form of government best adapted to our people, then you must regard the public school as the most fundamental concern of our society. Democracy well. Democracy will always call most of its leaders from the ranks of humble man, and to equip them It must provide free education to the sons and daughters of disadvantaged homes. Robert Jackson was born as you heard in 1892, I thought it was in Pennsylvania, not New York. Early in his life, the family did move to a farm in this area. His father was a farmer, a lumber man and a stock breeder. He advised his son Robert to become a doctor. Instead, on graduating from Jamestown High School, Jackson
A Tribute: Dean Ronald F. Phillips, Twenty-Seven Years of Leadership, Wisdom, and Devotion
As you step down after twenty-seven years as Dean of the Pepperdine School of Law, one can only think of your years there with awe. You have given the Law School its rightful place in the Sun. The quality of life for the law students is superb-a fine faculty, a supportive and caring administration, and a magnificent setting. You have brought many intelligent and interesting people there to speak to and interact with the students. You and your beloved wife were a “dream team.”
Few people survive and thrive in the difficult position of Dean of a law school for more than a few years. Your long service is evidence of your own personal qualities of cheerful disposition, optimism, caring, and energy. You leave big shoes to fill.
May your future years bring you a chance to share what you have learned with others so they may follow your splendid example.
Sandra Day O’Connor Associate Justice United States Supreme Court
Interview with Town of Paradise Valley Historical Committee
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR Tuesday, February 4, 1997 Joan Horne, former Mayor of the Town of Paradise Valley, and myself, Ann Townsend, are most privileged to interview Justice of the Supreme Court, Sandra Day O’Connor. Justice O’Connor, thank you very much for your graciousness in granting this interview in your home in Paradise Valley. Interviewer: Do we have your permission in quoting you in part or all of this interview for our project on the history of Paradise Valley, Arizona? O’Connor: I think we will do the interview first and then decide that. Interviewer: All right. Are you a native of Arizona? O’Connor: Yes and no. I grew up on the family cattle ranch in the eastern part of Arizona and the western part of New Mexico. The ranch was in both states. To get to the ranch house, we had to drive through miles and miles of New Mexico, before we crossed back into Arizona. The house was in Arizona. My grandfather started that ranch in 1880. That was where my parents were living when I was their first child. My mother wanted to go to the hospital for the birth of her first child, understandably. Her mother and father were living in El Paso, Texas, where my mother had lived before she married my father. Shortly before my expected arrival, my mother went to El Paso. I was born in Hope Will Do Hospital in El Paso. I understand that structure is no longer there. As soon as she felt up to travelling, she arrived back to the ranch with a relative, we got in a car and drove back to the Lazy-B
Acceptance speech for Janet Reno Torchbearer Award
Ruth Bader Ginsburg thank you so much because of the good job, I now hold, invitations come in abundance. To preserve energy and time for the courts heavy work, I must ordinarily just say no. For tonight’s celebration, however, I did not just say yes, I asked the women’s bar if I might have the honor of presenting the torchbearer award to Justice Sandra Day O’Connor. For all who know her agree: She fits the description to a tee. She is indeed a trailblazer. A grind human, whose mind carrying an incredible energy have encouraged women everywhere, to be brave. To appreciate their own worth, to aspire and to achieve. Sandra has been celebrated in many ceremonies. She has been praised for her independence, self reliance, practicality, and self possession. Of all the accolades one strikes me as describing Sandra best. Growing up on the lazy b ranch in Arizona. Sandra could ride a horse brand cattle driver tractor and fire a rifle with accuracy before she reached her teens, one of the hands on the ranch recalled his clear memory of Sandra Day. She was in the rough and rugged type. But she worked well with us in the canyons. She held her own. Sandra did just that at every stage of her professional and family life. The first woman on the Supreme Court brought to the conference table experiences others did not possess the experience of growing up female in the 1930s 40s and 50s. raising a family of doing all manner of legal work, government service, private practice successes successful
Juries: They May be Broken, But We Can Fix Them
Great Britain, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, and the United States continue to use juries to hear evidence and determine the facts in many criminal cases, although only the United States and New Zealand continue to require use of juries in most civil cases. Indeed, the jury system in this country is one of the most enduring aspects of our system. The only time most Americans, other than lawyers and litigants, see the inside of an actual courtroom is when they are called to serve as jurors. Juries have a proud history, both in this country and in England, where the jury as we know it developed. Juries usually do their job very well, and on occasion show extraordinary courage in the face of hostile or corrupt judges, delivering the verdict that justice demanded, even if it was not the verdict the judge wanted. As a trial judge, I presided over many jury trials in both civil and criminal trials. In all but two or three cases, I felt the jury reached an entirely appropriate verdict and the jurors were almost always conscientious and sincere in trying to do a proper job. But juries also have the ability to disappoint us, sometimes to the point of forcing us to question whether we should have jury trials at all. One of this country’s great observers of human nature, Mark Twain, once complained that juries had become “the most ingenious and infallible agency for defeating justice that human wisdom could contrive.” 1
Our federal Constitution and all of it state counterparts guarantee
Acceptance speech for American Bar Association medal
Sandra Day O’Connor Attorney General Reno, President Cooper, and distinguished guests and members of the American Bar Association. My feelings at this moment are of gratitude for this signal honor you’ve bestowed on me. And of amazement over the unlikelihood of at all, that a cowgirl from Arizona would have found her way not only through law school, but through 45 years of experience in the legal profession all the way to our nation’s highest court and to This wonderful honor tonight in the city of San Francisco. It was here in this city in 1952, that I was sworn in to the State Bar of California. And that lovely courthouse now restored for the Court of Appeals. It was just south of here in Redwood City that I persuaded the county attorney to give me my first job as a lawyer. Follow the road to this podium has in fact been a long one. It seems very short to me. It feels like only a few years ago, that law school opened my eyes to the world of the rule of law, to the intrigue of legal analysis, and the satisfaction of solving people’s disputes through negotiation. And when all else fails, litigation, the American Bar Association was in existence long before I entered the legal profession. It’s been working throughout my years as a lawyer to study and analyze different subject areas of the law and to propose and help achieve improvements. It has been a strong supporter of a qualified, competent and independent judiciary. It has worked hard to support adequate compensation for
Speech to American Bar Association Annual Convention on efforts to assist emerging democracies in central and eastern Europe
Unknown Speaker Well, I always thought I was the perfect person to introduce Justice O’Connor, because although it might not be obvious, if you look at our resume side by side, she and I do share two very important qualities. First, we are both women of the Southwest. Secondly, we have the most marvelous patient husbands on the face of the planet. Unknown Speaker But the other reason, Justice O’Connor that I assumed that I was given the honor of introducing you today is that although you don’t know it, you look over my shoulder every single day at work. One of the pleasures of being a president of the American Bar Association is that you meet magnificent people from all over the world. And very often you have your photographs taken with them. I’ve even had my photograph taken with Mickey Mouse. But I have only one picture of a famous person in my office. And it isn’t with me. It’s looking at me right above my desk, behind my chair. When I come into my office and Albuquerque every morning and turn on the lights and pull up the blinds. Justice O’Connor is looking right at me with her very direct gaze, that Brooks no dilly dallying, and says to me every day, I expect you to do more than your best because your best isn’t quite good enough. I know that you will hear this afternoon when Justice O’Connor receives the ABA medal about her magnificent contribution to American jurisprudence. And introducing her today. To all of you who care so deeply about the cause of democracy around
Speech to International Association of Lawyers
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you so much. Thank you. Thank you President Venugopal. I have the privilege of meeting your president Venugopal in India a couple of years ago when I went to give a lecture there named for his father, who was also a most distinguished attorney in India. And I’m so pleased to be able to come here to this wonderful city of Philadelphia tonight. The birthplace of our nation’s constitution and an absolutely wonderful city. So you chosen a great place for your making. Technology is constantly shrinking our world. From cellular phones to fax machines, beepers to email, satellite communications to the internet. new forms of communication have enabled us to talk to each other, whenever and wherever we happen to be. But it takes more than technological capability to enable people from different nations to communicate effectively with each other. People from all nations need language skills, they need a deeper understanding of foreign cultures, and they need deeper familiarity with foreign traditions and values. A nation’s ability to meet these needs will largely determine its ability to cope, and what has become an increasingly multinational environment. The United States is just beginning to recognize these needs. High Schools here, which wants only talk French and Spanish, as foreign languages now offer Russian, Japanese, Chinese, Arabic and a host of other languages as well. American businesses have also responded to the increasing globalization of brain,
Professionalism
It is a great pleasure to be here at Washington University to dedicate this magnificent new home for the law school. Winston Churchill once said that “[w]e shape our buildings and afterwards our buildings shape us.”1 Here you
have shaped a beautiful site, commensurate with Washington University’s reputation and equipped to meet the demands of contemporary legal education. I expect that this stunning facility will in turn inspire innovative scholarship, and nurture young lawyers with the finest legal skills and the highest professional standards.
As lovely as it is, what I would like to talk to you about today is not your new building. I would like to discuss my granddaughter. You see, I recently returned from an extended period of grandmother-granddaughter bonding sort of a cross-generational in-the-family version of Thelma and Louise and she is often on my mind. At one point during the visit, my granddaughter came to me, disappointed about having to perform some task or another. It was pointless, she said. Well, she didn’t actually say ”pointless.” Pointless, in the vocabulary of a young child, is replaced by two words: ”But why?” Her meaning was clear nonetheless. Her second objection was that it was “no fun.”
“Pointless and no fun,” one of my friends quipped. ”If those were
legitimate objections, we wouldn’t have anyone practicing law.” The comment seemed funny at that moment, but in retrospect it seems disconcerting. Is that what the practice of law has become-pointless
Introduction to a speech on the life of President and Chief Justice William Howard Taft
Unknown Speaker Society. Professor post lecture runs for an hour and 15 minutes and followed production by Justice Sandra Day O’Connor Sandra Day O’Connor am so pleased that the Supreme Court has or Historical Society is sponsoring this series of lectures on former chief justices. Now I have a special interest, of course, justices, but I think everybody should. And what really pleases me is that the lectures are held in this court room, and especially tonight going to hear about Chief Justice William Howard Taft. I mean, what better for us to hear about Taft, he was the person that thought Supreme Court should have a home of its own, instead of meeting in the basement in that Burt over in the capital that most of you have visited and he thought we had Court and a building of our own. And it had been talked about day but never approved, and Taft as the only person to ever President of the United States and later as Chief Justice, still have some clout politically with the Congress. He persuaded Congress to appropriate money for this building. And Taff did more than that he hired the architect for it, Cass Gilbert, and he was influential in forming the design and getting it carried out. I think we have one of the most wonderful buildings in all country, inspired every single day when I walk in here, and so it is special that we’re in this court room that Taft helped make possible to here at this lecture. I think there have been two chief justices who really deep About judicial
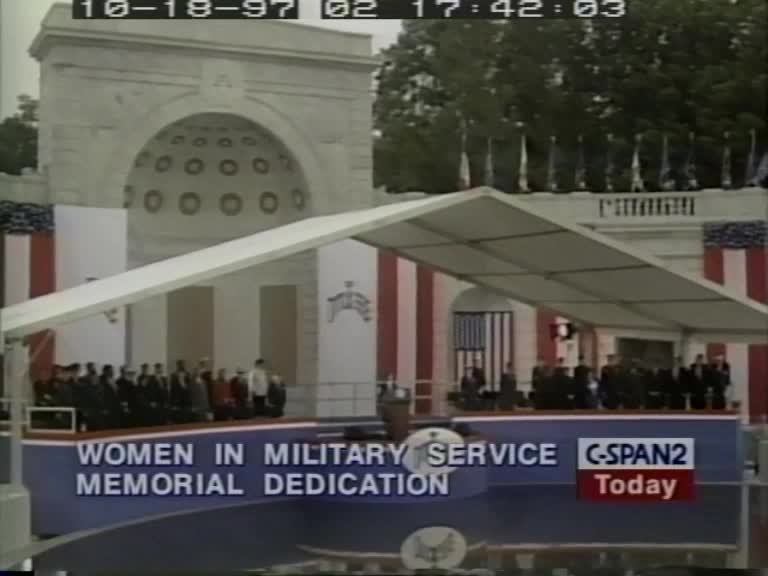
Remarks at dedication of Women’s Military Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery
Sandra Day O’Connor Secretary Cohen, General Vaught, distinguished guests here today and women of the United States military service. This is such a special moment, and a very proud day for women. I’m here today, not as a member of the military service, not as a veteran, but as a woman, as a grandmother, and perhaps as just a judicious observer. From the American Revolution, to Operation Desert Storm women have served in the military for most of the nation’s history. That service was unauthorized and carried out by women as volunteers, sometimes disguised as men. Approximately 127 women fought and skies is soldiers in the Civil War. After a century beginning in 1901, the United States Army established an auxiliary for nurses. Women did not become a permanent part of our armed services until 1948. But their number was kept 2% of the active duty force. That ceiling was lifted in 1967. Today, women represent about 11% of our armed forces. Some 211,000 women are on active duty, and there are some one and a half million American women who are veterans of the military service today. It is time indeed that we dedicate this splendid memorial to the women who have served in the military. As major Beatrice hood stroke, put it This isn’t just my brother’s country or my husband’s country, it’s my country as well. Indeed it is. Women have taken their places and all fields of endeavor in this country, from outer space to ocean depths, from battlefields to Court Room benches, from Chow lines
“Fiftieth Anniversary Remarks”
Fifty years ago, Stanford Law School began a transformation from regional respectability to national preeminence. A central rite of passage in the school’s progression was the establishment of the Stanford Law Review in 1948-an event made possible by the presence of an enterprising group of students, some dedicated young faculty members, and a new dean. The year that the Class of ’49 embarked on their legal studies at Stanford, Dean Carl Spaeth began his stewardship of the law school. It soon became apparent that founding a Law Review would figure prominently in the new dean’s vision for Stanford’s future.1 Once he obtained the unanimous support of the faculty, he called upon Charles Corker and John McDonough, two young professors with previous law review experience, to guide the new venture. They played the role of senior editors for an Intramural Law Review that served as a training vehicle for the first editors. As John McDonough has described:
By precept, example, and the time-honored process of remorseless, word-byword editing of student manuscripts, they sought to instill in the neophytes of ’49, who would edit Volume I, those standards of excellence in research and analysis and of meticulous care, if not obsession, with detail, citation, and language that are the hallmark of a first-rate law review.2
The Class of ’49 itself was an unusual group of students: Many of them had recently returned from military service, some of them were older than their predecessors had
On Federalism: Preserving Strong Federal and State Governments
Most Americans recognize the term “federalism,” but an exact definition of the term is elusive. Disputes over the bounds of state and federal sovereignty implicate “perhaps our oldest question of constitutional law.” 1 I propose that recent decisions of the Supreme Court indicate the emergence of a definition of “federalism” that may guide legislators and judges in solving national and local problems in a spirit of cooperation.
Our country has come a long way since its most early days, when Federal power over individuals was severely constricted because the Articles of Confederation required the cooperation of state legislatures in achieving national goals. The Framers resolved that problem by permitting the Federal Government to act directly upon the people. In my view, the allowance for federal regulation of individuals and protection of their national interests, while preserving the sovereignty of States acting within their own boundaries, is crucial to our constitutional framework.
The Framers recognized the need for a strong and functional government, but, as Justice Harlan once explained, they “were suspicious of every form of all powerful central authority.”2 By establishing two levels of government, the Framers sought to guarantee both national unity and individual liberty.
The framework they designed seems so deceptively simple that the Tenth Amendment has been described as “but a truism.” 3 Nonetheless, “the task of ascertaining the constitutional line between federal
Acceptance speech for Ellen Browning Scripps medal for women’s archievement
Sandra Day O’Connor Well, I’m all weighted down now with this fantastic medal. And my husband and I are so happy to be at this beautiful campus today and what a day you will produce for us. It’s incredible. We don’t have days like this in Washington DC. We can even see the snow capped mountain Mount Baldy. MM, this gorgeous campus. And we’re thrilled to be here and I’m so honored by the presentation to me today of the LM browning scripts award. You know Ellen browning scripts was a very special moment. When we look back and try to identify those women who’ve made a significant difference for the lives of all women who follow. We would include Ellen scripts on our short list. She lived a simple, brutal life, obtained an education largely by our own efforts eventually helped her brothers found a newspaper Empire and Layton life founded this very college Scripps College for Women. She had no money to go to college, and worked for two years to pay the cost of going to Knox College back in 1856. She graduated and became a teacher. She saved money has a teacher and moved to Detroit and help her brothers establish a newspaper. She even wrote a newspaper column as you’ve already heard. For many years, it was called Miss Ellen’s miscellany. She moved to California in 1890, where she remained until her death at age 96. All of her resources, which were considerable and time, she gave to charitable causes which interested her. She’s been described as a person who was a principal architect
Remarks at the awards ceremony for the national finalists of the Center for Civic Education’s We the People program
Sandra Day O’Connor This is the most impressive group all assembled to work and think and celebrate the Constitution. And I’m really pleased to have a chance to stay at say a few words to you tonight about justice, which is a very elusive concept. And it’s been the subject of human aspiration throughout the history of the human race. 1998 marks the 200 and eighth anniversary of the adoption of the Bill of Rights. Our Bill of Rights comes closest to our American notion of personal freedom and justice. And my appreciation for the Bill of Rights. It’s understandable because I spend a significant portion of my life working life thinking, arguing and writing about what it allows the government to do and what it does not allow. And yet after 17 years as a Supreme Court justice, I’m still awed by that document adopted 208 years ago. It’s as vital and timely today as it’s ever been. And I want to talk just a little bit about the history of the Bill of Rights, how it came to exist, and how our perspective on it has evolved. It was June of 1789 when James Madison stood up in the House of Representatives, and gave the speech in which he set out his first draft of what would eventually become the Bill of Rights. What prompted him to do that? History tells us that the Bill of Rights was not an accident. It represented the culmination of a long standing struggle between two groups. Trying to find the proper balance between the rights of individuals and states and the need for a strong central
Remarks at funeral of Justice Lewis Powell
We are gathered here today to remember and to celebrate the life of Lewis F. Powell, Jr. Last week Lewis left us and went home to God and to rejoin his beloved wife, Jo. I was at the Supreme Court in January 1972 to witness the investiture of Lewis Powell and William Rehnquist. I met the Powells at the reception following, but little did I dream then that I would know Lewis Powell as a colleague on the Supreme Court nine years later.
Justice Powell was the ninety-ninth Justice to serve on the Supreme Court and perhaps the most reluctant. It is reported that, on the day in January 1972 when Lewis was sworn in, Nan Rehnquist asked Justice Powell’s wife, Jo, if it wasn’t the most exciting day of her life. Jo reportedly said, “No, it is the worst day of my life. I am about to cry.” Lewis Powell had turned down an appointment to the Court in 1969 and was prepared to do so again in 1972. Luckily for the Court and the Nation, he finally agreed to accept the nomination when President Nixon convinced him it was his duty to his country to do so.
His family dates back to Thomas Powell who came to the James River area of Virginia from England in 1635. Lewis was born in Suffolk, Virginia, but lived most of his life in Richmond. He was an able student and a good athlete – playing basketball and baseball. He learned how to shoot and enjoyed hunting. He also learned as a youngster the demanding nature of life on a farm – his father bought a milk cow named Mollie. Lewis was directed to feed
Broadening Our Horizons: Why American Lawyers Must Learn About Foreign Law
Feature
Worldwide Common Law Judiciary Conference
BROADENING OUR HORIZONS: WHY AMERICAN LAWYERS MUST LEARN ABOUT FOREIGN LAW
A Commentary
We live in a world that is constantly shrinking. Cellular phones, fax machines, beepers, e-mail … all of these new forms of communication have made it much easier for us to talk to each other, no matter where we are in the world. We need, however, more than technology to communicate with people from other nations. We need language skills; we need deeper understanding of foreign cultures; we need to know how to survive in an increasingly multinational environment. Many of our schools recognize this need, and many parents are taking great interest in language training. High schools now offer more than French and Spanish. They are adding Japanese and Russian, as well. American businesses have been in the forefront of this move towards what newspapers constantly herald as the “globalization” of trade. There are McDonald’s restaurants in Moscow, and Kentucky Fried Chicken franchises in Beijing.
American judges and lawyers, however, sometimes seem a bit more insular. We tend to forget that there are other legal systems in the world, many of which are just as developed as our own. This short-sightedness begins early in our careers. We learn in law school to look first at the decisions of our own state courts. If we appear in federal court, unless the Supreme Court has spoken to an issue, we look to the law of our local circuit and, perhaps, district.
Speech to American Bar Association on law and national security
Unknown Speaker Ladies and gentlemen, if you please. I’d first before introducing Justice O’Connor, I’d like to just say a brief word about the special edition of the National Security Law Journal, which is here on the tables. That includes, among other things, the eulogy that Justice O’Connor gave at justice, palace funeral, and a number of other remarks. And justice pals honor and in as much as this is a special tribute to him. This this dinner this evening. I like to thank every meeting of this committee as a tribute to him. But this is a special tribute. I invite you to pick a copy up on your way out and make it part of your power collection. I’m particularly pleased to have been given the assignment to introduce Justice O’Connor, to the family, to the committee and to its broader family. In part two, because of the special place that she had in the affections of lewis powell and the special esteem the professional esteem that he had for her. I’ve been instructed to make my introductions snappy, she shakes her head. And therefore I won’t pause long over the record facts which are well known but quite astonishing. So I’ll just glide by them quickly. Coming off a large cattle ranch near the New Mexico border, growing up there getting to Stanford at age 16. If I counted correctly, getting both her bachelor’s degree and Law Degree in six years. I think I’m right about that. finishing third in her class, and then finding herself unable to persuade any top law firm on the west
Conversation with Justice Stephen Breyer and high school students on how the Supreme Court works
Sandra Day O’Connor Are we in communication now with O’Connor high school? Unknown Speaker Yes, ma’am. Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. Okay. I’m Sandra Day O’Connor, an Associate Justice here at the Supreme Court. And I’m appearing here this morning with my colleague, Justice Stephen Briar. And we’re delighted to have this hour to spend with some students and talk to you a little bit about what we do and what it is. The Supreme Court does, and I think we’re going to start off with Justice Briar, because he has done this program once before, so he’s had all the experience and we’re going to start off with justice Briar. Right? I’d like but you’re in the Benjamin Banneker academic High School. Stephen Breyer All right over there. We have the Mount Vernon High School over here. Good. And we have the Sandra Day O’Connor. Hi. I haven’t forgotten the honor High School. Down here. Is that right? Yes, they say that they’re there at a long distance there in Texas. That’s right. Very lucky there. And I guess it’s the the 10th 11th and 12th grades 12th grades 11th grade, just 12 fine. Okay, then your experts. All right by this. Let me Can I ask you a couple of questions of what your idea is. I would like to know if somebody says to you now there is a legal case going on a case of law. In a court, what do you think it could be about? What are the what kinds of things? Could it be about? This Any question? Anything can be anything it could be about? copyright, it could be about copyright.
Speech at dedication of Western Justice Center Foundation
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. Thank you. Thank you so much. Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you judge Nelson, for that very splendid introduction. You can just see why it’s been so terrific for the western Justice Center to have just judge Nelson involved. Because talk about a bundle of energy. And you can’t tell her No. I mean, there’s no such thing. So she has a tremendous asset. And President Donald Baker who has provided such Distinguished Public Service in Los Angeles County, along with his legal work, and I know what an asset he’s been to this institution, and Bill Drake, who was captured from a dispute resolution facility in Washington DC to come out here. And I think that was a great asset. And my boss back here, Chief Judge Proctor hug. I’m the Ninth Circuit justice. So I have to do what he says we’re in the ninth circuit here. And so. So he’s been a great Chief Judge, and how fortunate it is that he also is involved in this marvelous project that was initiated really by the first efforts of the Ninth Circuit judges, we’re going to occupy this wonderful building. You know, the original Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals Court building is that fantastic facility in San Francisco that was damaged so badly in the last earthquake, but is now restored at a very high price, taxpayer dollars, but it’s it’s love light. And the Court of Appeals judges from Southern California used to have chambers and work in downtown Los Angeles. But the old this stuff, but they call it this stuff,
Speech at National First Ladies’ Library awards dinner
Sandra Day O’Connor Mrs. Clinton, Secretary Albright, Mary Regula, Wendelyn Brooks Elizabeth Campbell, Shirley Chisholm, thank all of you for this wonderful honor and this very delightful evening. Although I was the first woman to serve on the US Supreme Court, the credit goes not to me, but to the thousands of women before 1981, who demonstrated that women can do a good job in any field of endeavor. And all those women who spoke out forcefully in seeking equal opportunities for women in the workplace in my lifetime, not just in yours, Elizabeth Campbell, but in my lifetime, too. We’ve seen extraordinary improvement and opportunities for women. These changes have been good for women, and they’ve been good for our country. Congratulations, Mary, on the establishment of the First Lady’s Library. Americans admire their first ladies so much, and all of us will welcome this institution dedicated to preserving the record of their achievements. Thanks for making this such a special evening.
Remarks to National Center for State Courts on public trust and confidence in the justice system
Unknown Speaker Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you very much, Chief Justice Lackett of my home state Supreme Court, Chief Justice Veasey of Delaware with whom I had the privilege of being with back in November when I went to Delaware for an event of the state bar there. And all of the chief justices, justices, judges, great Americans and others here at this conference today, I’m so glad to be with you. But I’m also very nervous because I haven’t been able to attend your conference. And I told Tom’s Lakha that I thought I had a lot of nerve to come here and talk to you on your last day when I didn’t know what you would been talking about. And I hope you will Give me because I haven’t been privileged to be part of your conversations and I surely wish I had, because there’s a lot I could learn. And I’ve been a little bit out of touch with things in the state court systems lately, as you might have noticed. So I think those of you here are in tune with what’s going on much more than I am. I work in a building which bears a marble inscription over the entrance that says equal justice under the under law. The subject of this conference shows an admirable awareness of the importance of public trust as a dimension of equal justice. This is the first national conference on this subject, and it’s very impressive that so many state Chief Justices and state court administrators are here. Also impressive is the hosting array of National Court organizations, the American Bar Association, state
Commencement address for Washington College of Law
President Ladner and Dean Grossman, and faculty graduates and friends of Washington School of Law. What a special day. This is for all of you graduates of the American universities, Washington College of Law, and for your families who helped you to reach this day and this moment, it has taken each of you at least three years and perhaps considerably more of law school studies to enable you to obtain your law degree today. You will have no more lectures and exams to endure.
And the faculty will no longer have you to endure. You will presumably begin to use your legal training in a variety of ways. Someone private practice, summon the public sector, summon business or a non legal pursues, but your thought processes, the way you approach and analyze problems is now forever changed. You’ve learned to break down complex issues into their component parts, and to look at them with some detachment and objectivity. You’ve learned how and where to try to find some answers. These are not insignificant achievements.
Now, it’s a special day for me as well. This law school, as you know, was founded 103 years ago, in 1896, 24 years before women had the right to vote. Founded by two determined women, Ellen Spencer Mussey and Emma Gillett. Its first students first read, we’re women. Since its beginning, the Washington College of Law has valued the role that women as well as men play as lawyers in our society. It has provided strong clinical programs to give students hands-on experience, helping those
Panel discussion with Justice Stephen Breyer and judges from the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals
Stephen Breyer Justice is Sandra Day O’Connor and Stephen Brier participate in a question and answer session with judges of the ninth us Circuit Court of Appeals. This event took place at the circuits annual Judicial Conference held this year in Monterey, California. It lasts an hour. Unknown Speaker Judge case and mythos p&i are the live in the water be at the opportunity to carry on this conversation with our justices. I’m not going to make any elaborate introductions. All I’m going to say is this is not Judge Judy, and matters not judge Walker. Unknown Speaker The usual custom. We’re going to start off with a question to the junior justice. Unknown Speaker Several factors influenced the members of the conference. But to choose, as the theme for this conference, the importance of the independent judiciary in securing a free democratic society for its citizens. Many of us have had an opportunity to observe firsthand the corrupt and proven sighs legal systems of the country’s emerging from dictatorial systems, the contrast to our own legal system, but home the preciousness of our system, and we have the striking criticism of judges by politicians on both sides of the aisle. The bear incident was produced over judicial confirmations have suggested that we need to pay heed preservation of our own independent judiciary asking just just prior to see a real threat to our traditional independence, or is this just business as usual? And do you have any suggestions as to how we might
Room for Improvement
Room for Improvement
Although public confidence in the justice system is relatively high, several aspects of the courts call for reform
I work in a building that bears a marble inscription over the entrance that says “Equal Justice Under Law.” Everyone involved in our profession (including law students preparing to enter it) would do wen to remember that public trust in the justice system is critically important as a dimension of equal justice under law.
Two 1999 national surveys by the American Bar Association and the National Center for State Courts reveal a fairly high level of public confidence in our courts. There is a widely held belief that, although not perfect, our justice system is one of the best in the world. The public’s faith in our system has in creased over the last 20 years, even as confidence in other public institutions has.declined. But the surveys also show substantial dissatisfaction in some areas.and many opportunities for increasing public trust in the justice system.
Among the areas that affect public attitudes toward the justice system are Juvenile and family courts, bias in the courts and court-community relations, the jury system, and access to justice-issues of my own longtime concern.
Many other issues are certainly as import.ant My failure to include them here by no means indicates that I consider them unworthy of attention.
The first item on my list of concerns is the need to strengthen juvenile and family courts. This need often has been
Speech at dedication of new building for University of Oregon Law School
Unknown Speaker I hope you all have a wonderful afternoon the meeting is adjourned. And Unknown Speaker you’re watching c spans America and the courts. Next associate Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O’Connor helps dedicated new building at the University of Oregon law school and Eugene defense about 25 minutes. Unknown Speaker It is rare that a speaker so perfectly fits the occasion, as does our speaker in this dedication. As we dedicate to Wm W. Night Law Center, we do so building on a legacy of qualities that we aim to carry into the future. qualities that have served our state so well, and qualities that will continue we hope to do so. There are many but I think particularly of three that are most applicable today, a pioneering session spirit of boldness in thought and action, and a wisdom that is deep and lasting in its vision. Since our beginnings as Law School of the West, the University of Oregon School of Law has worked hard to be at the forefront of legal needs and new areas of practice, not content simply to follow, we have aim to lead and to prepare legal practitioners to do the same. Along with this pioneering leadership, we’ve encouraged the boldness of thought and action, and ability to move beyond the ordinary two ways and means of achievements not yet considered, let alone practice. This has been a Center for Public Service and law reform. And we’ve encouraged and nurtured a worldview that sees beyond letters to the words beyond words to the entire text, beyond
The Legal Status of Women: The Journey Toward Equality
Sandra Day O’Connor And welcome to all of you. I wish we had more space. But people like sometimes to visit the Supreme Court, and I feel very privileged that I could participate in this meeting today and sponsor the availability of these rooms for that purpose today. And you’re all most welcome here. And ambassador, maj to Ben, this is Laura and my fellow panelists here and distinguished guests.
It gives me great pleasure to be here today and to give remarks on a subject in which I take considerable interest, the legal and social status of women. I would like to thank Ambassador Mejdoub, the Hannibal Club, and the President’s Interagency Council on Women for providing this forum to discuss and promote women’s issues.
Women from all countries have much to share with each other about their own cultures, experiences, successes, and failures. Today, as always, women are the primary caregivers worldwide. We bear and nurture the children, and we manage the household for our families. But we also work outside the home. We want and expect to have equal opportunities in business, in the professions, and in public service. We want and expect to be paid as much as men for the same work. While women have made tremendous advances in this century, the process of achieving gender equality is still an ongoing one, in this country and throughout the world. In many respects, we have traveled far, although we have a way yet to go. We remember the old adage that “[t]he test of every civilization
Panel discussion with other justices at Stanford University Law School on the international role of the Supreme Court
Kathleen Sullivan (Dean, Stanford Law School) Thank you, Mr. Neil, for that extraordinarily generous introduction. Thank you Justices O’Connor, Kennedy and Breyer for gracing the stage and this illustrious event. Thank you all of you judges who stood a moment ago to be recognized not only for your attendance, you give us honor by your presence. But for your years of public service, all of you together do participate in what we must be proud of as one of the crown jewels of the American system of government, air independent judiciary, which is indeed the envy of the world. And that is really our topic today: the envy of the world. Why is it? What if anything, should we envy about judiciaries in other nations? And I would just open this discussion of comparative judicial systems, first by telling you a little bit about the people on this panel, and then by introducing the topic.
Let me remind you, as you already no doubt know about each of these wonderful justices from the western United States. First, that Justice Sandra Day O’Connor is twice a Stanford Graduate. She received both her BA and her law degree from Stanford. She was at the very top of one of the most talented law school classes ever in our holes, the class of 52, which also included the Chief Justice of the United States, William Rehnquist. While she was at Stanford Law School, Justice O’Connor was a member of the Law Review. And indeed, it turns out that she met her husband, John O’Connor, and spent some time doing
Panel discussion on U.S. and European Courts at Yeshiva University Cardozo School of Law
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you very much all. We’re not going to take much time now because we want to leave time for discussion. But I wanted to say how much it means to those of us in the United States that members of the European Union’s Court of Justice were willing to take the time in their break to visit this country to come to New York and visit us in Washington DC starting Tuesday and Wednesday, and then to have a state court experience when they conclude their visit in the state of Texas. And we had those of us in the United States learned a great deal from our visit to the European union summer before last. It was invaluable to those of us who were privileged to make that journey. And we’re just so delighted that you Paul and Judah and john Sexton and the others who have participated in making this visit begins so well in the city of New York. Thank you. And I think my colleague Justice Breyer has a word in French.
…
Sandra Day O’Connor It’s rather interesting because the concept of proportionality, as you described it, which you apply in looking at actions of the member states, resonates for us with the kind of language we use and applying strict scrutiny for an action, or eight that might be said to infringe some fundamental individual liberty in this country. That’s the same kind of inquiry we make. Whether it’s the least restrictive means whether it was necessary to achieve the objective, how important the objective was. These are the kinds of things we look
Commencement address at George Mason University
Thank you, President Merton, the Honorable Ed mace, and my fellow honorary degree recipients.
Now first of all, we have find out what are these privileges a permanent they are to President Merton. I keep hearing that, and I haven’t quite figured that out. It is an enormous pleasure to be here today at George Mason University. After all, it’s a day of joy for everyone. You graduates have no more University exams or classes to endure. And I might say the faculty no longer has you to endure. You have you have fame and fortune ahead of you, your family, spouses and friends can look forward to seeing more of you. And your speaker has the rest. But from her labor’s up on Capitol Hill, so it’s quite a day. Now, I realize we’ve gathered here today to applaud those of you who are receiving degrees. But there are a few other people here today who should also be recognized and with whom you graduates probably would like to share your glory. I refer, of course to the parents, spouses or other family members who have made some significant contributions to your presence here today. First of all, your parents have the brains which you were lucky enough to inherit. And your family probably provided at least some of the money you needed to sustain yourself while you were here. So I congratulate your families and command you graduates for your good judgment in selecting them. Now, a commencement speech is a particularly difficult assignment. The speaker is given no topic and is expected to be
Remarks at the American Bar Association’s Woman Lawyer of the Year award ceremony
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. Thank you. Thank you. Thank you. Thank you. Thank Thanks. Thank you so much. What a special day this is for all of your honorees and how happy I am to be in the company today with such a remarkable group of women honorees, I can’t imagine a better group and I have sat today fascinated with every single one of them and everything they had to say. I’ve heard how special this event always is. And I’ve not been able to attend all these luncheons, but I think I’m gonna have to come back because I grew up as a cowgirl in the southwest. And I learned out there that the only thing that mattered was whether you could lend a hand and do it well. It didn’t matter whether you were black, white, or brown, male or female, young or old, you’re just had to do your job. And it was a place where everything around you could hurt you. If you didn’t watch out. You could run into a rattlesnake. You shook your shoes out to get rid of the scorpions. Every time you fell off your horse, you were in danger of falling into a cactus. I mean everything out there could bite, prick, tear, cut, or whatever it was. And all I ever wanted to be was a cattle rancher. That was all I knew. My grandparents had done the same, and my family. And it’s been a long road from that dry, barren Southwest cattle ranch, to the marble courtroom, where I often find myself sitting today. It’s been a very long and often a very hard road for women lawyers, since Margaret brand became the first woman
Remarks celebrating the Magna Carta at the Runnymeade Memorial
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you President, Bill Paul, and the Lord Chief Justice Harry volts my friend from even before my days on the Supreme Court, and Lord justice Norse, it’s good to see you again. And to see all of the members and brands of the American Bar Association, who were able to come to this remarkable place today. I don’t know about you. But when I walked today, across this Meadow to this historic spot, I was deeply moved. This Bob resonates with historical significance to everyone here today. And every citizen of the United states and of the United Kingdom, and indeed far beyond the boundaries of those two nations. And it’s a wonderful privilege to speak today in commemoration of one of the most momentous occasions in legal history. In many ways, the story of English liberties, and therefore the story of American liberties began on this very meadow, when King john affix the Great Seal of the realm to the Magna Carta. In truth, the grievances of the barons who impelled King john to come here in June of that year, were rather mundane concerns the barons were generally unlettered and self interested man, who sought practical concessions from the king and return for their allegiance to the crown. The Magna Carta bottom is an intensely practical document. tailored to the problems of feudal times, spelling out one by one concrete remedies or actual abuses. But in addressing the specific grievances, the great chart or use language that transcended the barons parochial
Discussion at the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals Judicial Conference
Host Ladies and gentlemen, please take your seats. Ladies and gentlemen, will you please take your seats as we’re ready to begin the last segment of the program today. Thank you. Welcome to what has become a highlight of the Ninth Circuit Judicial Conference. And that’s our conversation with Justice O’Connor. Now based on what we heard from the last panel, the internet panel, I’m thinking that perhaps we can protect this segment of the program under a Judicial Conference methods patent, but we will leave that maybe for the Federal Circuit. Our panel this morning includes Chief Judge [Terry] Hatter from the Central District of California, Peter Benvenutti partner from San Francisco firm of Heller Ehrman and Professor Kathleen Sullivan, Dean of Stanford Law School. Although we are listed in the program as interviewers, I think that’s somewhat of a misnomer, because we don’t really intend to interview Justice O’Connor. The Sandra Day O’Connor that’s news to me. Host But you’re not off the hook because we will ask you some questions. We just won’t call them interviews. Courts last term certainly was an interesting one. And the cases resonated, I think, not only with judges and lawyers, but with the public at large. They dealt with everything from the Boy Scouts in the First Amendment, tobacco, the Violence Against Women in Act. Two, of course, Miranda warnings. Some of the legal commentators and pundits of which you know, there are many have called it a blockbuster term. I’m not
Speech at dedication of Sandra Day O’Connor Federal Courthouse
In October 2000, Justice Sandra Day O’Connor visited Arizona to dedicate two new federal courthouses: the Sandra Day O’Connor United States Federal Courthouse in Phoenix and the Evo Anton DeConcini United States Federal Courthouse in Tucson. The following is a compilation of Justice O’Connor’s comments given at the dedication ceremonies.
It is a great pleasure to be in Arizona this week to participate in the dedication of not one, but two, new federal courthouses-one in Tucson and one in Phoenix.
The dedication of the Phoenix courthouse is an occasion that has, for me, a sense of unreality. How is it that the name of a cowgirl from Eastern Arizona would be carved in stone on this large new federal courthouse in Phoenix? As many of you know, I grew up on a cattle ranch in Greenlee County, miles from any town. My ambition as a child was to be a cattle rancher like my father. That was not to be, and, in time, I entered law school at Stanford. I knew only one lawyer at the time. He practiced law then in Lordsburg, New Mexico, and years later was appointed a federal district court judge. I did not know where a law degree might lead.
When I graduated from law school in 1952, I received no offer of employment as a lawyer. There was one half-hearted offer of a job as a legal secretary. In time, I persuaded the District Attorney of San Mateo County to give me a job as a deputy. My career as a lawyer was launched. John and I were married, and within a year he was drafted, then accepted
The Supreme Court and the Family
REMARKS
THE SUPREME COURT AND THE FAMILY
Honorable Sandra Day O’Connor*
It is a true pleasure to be here at the University of Pennsylvania Law School’s sesquicentennial celebration and at the Family Law Symposium. The celebration makes me feel young-by comparison. It is appropriate that one of the centerpieces of your celebration should be this symposium on family law. The family is at the heart of American life, as well as American law. As Justice Powell wrote on behalf of the Court in Moore v. City of East Cleveland, “‘the Constitution protects the sanctity of the family precisely because the institution of the family is deeply rooted in this Nation’s history and tradition. It is through the family that we inculcate and pass down many of our most cherished values, moral and cultural.”1
It is this deep commitment to the family that has led so many of you to dedicate your careers to the development of family law. Family law poses special challenges and requires judges and attorneys, as well as other professionals like psychologists and social workers, to study and work together. And you must work together often-in 1998 alone, approximately five million cases involving domestic matters were filed in state courts.
The ultimate goal, of course, is to maintain and improve a legal system that protects and respects the family, both as a unit and as a group of individuals with their own rights and interests. It is not an easy task, particularly in light of the momentous changes
Speech at General Services Administration award ceremony for architects of federal buildings
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you so much, Mr. Anderson. And Acting Deputy Administrator bib and Mr. Kiss Delaney and my friend Bill IV. Now, they’ve already said everything I was going to say to you. So I’m a little bit of trouble. You know, there are about 370 federal courthouses in the United States. And there have been, as I count them, about 60 funding requests for new federal courthouse construction, actually approved by Congress in the brief period from 1986 to 2001. That’s a lot of courthouses, when you think they’re only 370 to begin with. And those funding requests total, by my calculation, about 501 million or half a billion dollars. Each of these projects has required architectural engineering, design, and other construction expertise, expertise of all kinds, which will be recognized today. I don’t know about you, I’m not talking to the architects now, because you probably already think this. But I place a very high value on architectural services. I care about my surroundings, whether it’s my home, or where I work, I feel better, and I work better. If I’m in a place that I think is handsome, and that I enjoy, it makes a real difference to me. I suspect it makes a real difference to everybody. And I think that good design matters in courthouses and elsewhere. It must, of course, accommodate the basic functional needs of the structure in a courthouse, that means court rooms. And I have to say they’re pretty know by and large these days, maybe you can figure out something
Altered States: Federalism and Devolution at the “Real” Turn of the Millennium
Sandra Day O’Connor Mr. Vice Chancellor and Lord Chief Justice, and my lord millet and Sir David and Lady Williams, Professor Smith and distinguished guests, friends of Cambridge.
It is my great honour and pleasure to deliver the inaugural Sir David Williams Lecture. Sir David is among the most distinguished members of the legal academy not only in this country, but around the world. His teaching career began at the University of Nottingham, after which he taught at the University that, I am told, is known affectionately in these parts as “the other place.” Sir David then joined the Law Faculty at Cambridge, later serving as the Rouse Ball Professor of English Law and President of Wolfson College. Sir David has been a path-breaker in the fields of constitutional and administrative law. His books, “Not in the Public Interest: The Problem of Security in Democracy”, and “Keeping the Peace: The Police and Public Order”, are landmarks in his fields and, I suspect, will be for a long time to come.
Sir David’s impact, however, is not confined to the life of the mind, but extends also to the world of public affairs. While enhancing our understanding of democracy, he has demonstrated a passionate concern for the quality of life in this democracy through his public service. He has served on the Royal Commission on Environmental Pollution, the Council of Tribunals, the Clean Air Council, and a number of other bodies whose work is significant. Sir David has also excelled as a leader
Roundtable discussion on Native American legal issues at National Judicial College
Host What you’ve seen in the last three days? What are your impressions? Sandra Day O’Connor I guess we’d both like to share some thoughts on what the impressions are. And it was a short trip. So I’m sure that what we saw is only a fraction of what’s available to see. And I would not think that we gained an insurer knowledge about anything, but we did have some impressions. And the first thing my I noted is that nothing in Indian country is said briefly. And the second thing is that if you’re going to visit Indian country, you have to be prepared to eat heartily. And I noticed I have to confess a general unhappiness with some recent Supreme Court jurisprudence in the area of Indian law. I think that was clear. We also saw a tribal court system in a small tribe setting in the Spokane tribe, and a tribal court system in a very large setting in the Navajo Nation. And the tribal courts that we saw small and large, were functioning and functioning very well. The Navajo court is suffering from a horrendous caseload. Well over 70,000 cases annually And 14 trial court judges now how can you have the left and the facilities in Window Rock, which is probably the best facility? We’re limited. So here are judges in need of some additional judges and some enhanced facilities. I think, nevertheless, we met some wonderful judges in, in both tribal court systems that we saw, and people who cared and are determined to function well, and it was very impressive to see that. And we saw some real
Speech at groundbreaking ceremony for New York University Law School’s new building
Unknown Speaker Justice Sandra Day O’Connor is next. She recently spoke at the groundbreaking ceremony of New York University Law Schools new building in Manhattan. She reflected on the American spirit after seeing the ruins of the World Trade Center. Unknown Speaker When we scheduled this event, there was only one person our community wanted to deliver the principal address. Remember the faculty lunch at which she spoke to us that stimulated the idea for a conference that just the other day as we celebrated the success of the global law school initiative, was referred to as the seminal intellectual event of that program, now widely recognized as having transformed all of legal education, not just this law school. But Justice Sandra Day O’Connor didn’t just do that one act of beneficence to this school. She has been an integral part of this law school community at every turn. She has visited our campus during my time as Dean, this is now I think, her seventh time. And every time she comes, she meets with faculty as she will today. She meets with students as she will today. And she enhances our world. But equally, she’s been there as counselor and advisor throughout the evolution of this law school. There is no one outside of the immediate law school community, who is a great friend to this law school, and Justice Sandra Day O’Connor. And I’m delighted to introduce her to you today. Justice O’Connor. Unknown Speaker Thank you. Thank you. Thank you. Thank you. Unknown Speaker
Discussion on the state and federal judiciary systems with the National Association of Women Judges
Susan Herman
Let me say to start that I cannot claim to be a non woman, but I certainly can claim to not be a judge. And I’m looking at the three pictures in the program. I thought, well, you know, law professor takes you pretty far when you’re the front of a classroom. But yeah, I was feeling said about ranked until my daughter said to me, Mom, for tonight you can outrank anyone, you’re Oprah.
Judith Kaye So I let’s talk
Susan Herman
I guess we’ve all been around court circles long enough to know that you never get to start by talking to the judges on the highest court first. So I would like to ask judge Kaye to start us off our reminiscences by reminiscing, your husband referred to your decision to go to law school. Would you like to share some of how you went into the law and why you decided on that?
Judith Kaye
May I say, first, that I think the evidence is incontrovertible that I married very well. Excellent. And indeed, I I never, never for a moment growing up, wanted to be a lawyer. In fact, I did grow up as you’ve heard so much about me already in a small community. I think there was one woman lawyer there once but I never saw her. Talk about private people. So being a lawyer was not something I ever saw or aspire to infect. What I aspire to was a career in journalism. I sort of saw myself as critic of the decision makers. That was what I yearn to be. But it was impossible to find work back in the year 1958 when I graduated, just like you from Barnard
Recording session for Lazy B audiobook
NBC interview with Katie Couric
Katie Couric To many, Justice O’Connor has been an icon of intellect and equality ever since she took her place on the bench more than 20 years ago. But sitting down with her I also found a humble, relaxed and at times very funny woman who readily admits to once having some mixed feelings about her place in history. Sandra Day O’Connor The phone rang and it was President Reagan. Sandra. I’d like to announce your nomination to the court tomorrow. Is that alright with you? And I didn’t know if it was it or not. Katie Couric For Sandra Day O’Connor, it was hard to believe the choice was hers. She could become perhaps the most influential woman in the country. But she wasn’t so sure she was the right person for the job. They were scared. Sandra Day O’Connor Yes, I was concerned about whether I could do the job well enough to deserve saying yes, Katie Couric a very rare and candid admission from a member of the most exclusive and reclusive club in America. The first woman on the Supreme Court is a pretty daunting title. Did you think about how important that was for women everywhere? Sandra Day O’Connor Of course, the minute I was confirmed, and on the court, states across the country started putting more women on and had ever been the case on their supreme courts. And it made a difference in the acceptance of young women as lawyers. It opened doors for them. Here we go. Okay, so Katie Couric Sandra Day O’Connor has been opening well, gently pushing doors open all her life,
Interview on PBS NewsHour
GWEN IFILL:
The book is Lazy B: Growing up on a Cattle Ranch in the American Southwest. The author is Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O’Connor. Justice O’Connor, of course, was the first woman appointed to sit on the Supreme Court. But long before she got to Washington, she lived a life we read about only in westerns. In Lazy B, she joins her brother, Alan, in recalling their memories of those times. Welcome, Justice O’Connor.
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR, Author, Lazy B:
Thank you. Well, it is a joint effort with my brother, Alan. And Alan ended up running the ranch for most of his adult years. And so he had lots of institutional memories of that amazing place.
GWEN IFILL:
Well, tell us about the ranch, for those of us easterners or those of us who aren’t native to the Arizona-New Mexico border.
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR:
Well, it’s… It’s in the semi-arid high desert plateau region on the New Mexico-Arizona border, along the Gila River. And it gets very little rainfall a year, about ten inches a year — about 5,000 feet in elevation, other than the higher mountains to the South. And it’s just… It has a subtle beauty that the desert can have. But it’s maybe difficult for someone in the Northeast who’s used to seeing greenery all the time to appreciate that desert scene.
GWEN IFILL:
What was unique about growing up on a ranch like that?
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR:
We were isolated. We had no neighbors, really. It was 35 miles to town. We would go to town once a week to get the
Speech at Dedication of Clara Shortridge Foltz Criminal Justice Center
“It is too bad, daughter, that you are a girl, for if you were a boy, I would educate you for the law-you would make a great lawyer.”
Lazy B: Growing Up on a Cattle Ranch in the American Southwest
Professionalism: Remarks at the Dedication of the University of Oklahoma’s Law School Building and Library
It is a great pleasure to be here at the University of Oklahoma to participate in the dedication of the new building and library for the College of Law. You have created a beautiful, state-of-the-art facility, equipped to meet the demands of contemporary legal education and befitting the University of Oklahoma’s excellent reputation. It is bound to inspire academic achievement, nurture interesting and valuable scholarship, and nourish a sense of community among the school’s students, faculty, staff, and alumni.
When David Boren decided to leave the U.S. Senate, John and I and people across the land were sad and disappointed. As a Senator, David Boren made great contributions to good public policy and understanding. Now that I have seen his accomplishments here at the University of Oklahoma, however, I can understand his satisfaction in seeing tangible results from his leadership and efforts. Those results are everywhere across the campus. After visiting the Reading Room and the Student Union today it made me want to be a student again and right here at this University. The Oklahoma Law Center had a direct effect on my study of the law. One of this law center’s professors in the 1930s and 1940s was Marion Rice Kirkwood. He left and went on the Stanford law faculty. He taught me real property and water law at Stanford Law School and he served as Dean of Stanford Law School for some years.
This Law Center is fortunate indeed to have Andrew Coats as Dean. He has made a real difference
Speech at the American Law Institute annual meeting
Sandra Day O’Connor Now on the whole, the United States judicial system leaves a favorable impression around the world, but in the treatment and United States Courts of international law there jury is still out. Because of my exposure to a great many legal systems around the world. I decided to speak to you today about the need for more knowledge about international law and transnational law. Why does information about international law matters so much? Why should judges and lawyers who are concerned about the intricacies of ERISA and the Americans with Disabilities Act and the bankruptcy code, care about issues of foreign law, and international and transnational law? The reason of course is globalization. No institution of government can now afford to ignore the rest of the world. The importance of globalization should not be underestimated. 30% of our gross domestic product is internationally derived. We operate today under a large array of international agreements and organizations, the UN Convention on contracts for the International sale of goods. NAFTA, the World Trade Organization, the Hague conventions on collection of evidence abroad and service of process. And the New York convention on horsemen of arbitrage rewards dimension only a few. But globalization is much more than these agreements and organizations. It also represents a greater awareness of and access to people, some places are different from our own. The fates of nations are more closely intertwined than
“William Howard Taft and the Importance of Unanimity”
William Howard Taft and the Importance of Unanimity∗
This Term, the Historical Society has put on a wonderful series about the man who is widely—and rightly—regarded as this Court’s greatest Chief Justice. Through his recognition of the right of judicial review, John Marshall secured for this Court a role in shaping the nation’s most important principles: racial equality, individual liberty, the meaning of democracy, and so many others.
Learning more about John Marshall this Term has caused me to think about another great Chief Justice, who perhaps deserves almost as much credit as Marshall for the Court’s modern-day role, but does not often receive the recognition: William Howard Taft. Taft, of course, was remarkable even before he became Chief Justice—but even the presidency did not hold as much charm for Taft as did his eventual position on the Court. Mrs. Taft noted in her memoirs that “[N]ever did he cease to regard a Supreme Court appointment as vastly more desirable than the Presidency.”1
Mrs. Taft, however, disagreed. She loved being First Lady, and was a good one, at that. She was responsible for bringing the cherry blossoms to Washington, a feat for which I am particularly grateful. She also made a bit of history on March 4, 1909 by becoming the first First Lady to accompany her husband from the Capitol to the White House on Inauguration Day.2 She was a difficult woman to refuse.
Taft, on the other hand, was an unpopular President. His bid for re-election was
Copyright Law from an American Perspective
HISTORY OF AMERICAN COPYRIGHT LAW
I want to speak today about the history of copyright law in the United States and how that history compares with that of copyright law in Ireland. The history of copyright law in my country is not so different from yours. For one thing, both of our laws have been written in English. Unfortunately, that hasn’t made either of our laws easy to read.2 More seriously, our two sets of laws share a common ancestor-the Statute of Anne, passed by parliament in 1710. Before the Statute of Anne, only the publisher of an author’s writings had the right to issue copies of those writings, and held those rights in perpetuity. The Statute of Anne granted initial property rights in literary works to authors, who could then sell those rights to publishers. The Statute also limited those property rights to a period of up to 28 years. Finally, the Statute of Anne only provided remedies against the literal copying of protected works.3
The Statute of Anne remained the law in the American colonies until the United States declared independence in 1776. Soon after, the United States adopted its current Constitution. That document established a national government with a limited set of powers. The powers of our national legislature, the Congress, are enumerated in Article I. Among the legislature’s powers is to “To promote the useful Arts…, by securing for limited Times to Authors… the exclusive Right to their Writings… ” 4 Under our system, our legislature-the
Vindicating the Rule of Law: The Role of the Judiciary
The last two decades have witnessed a remarkable transformation in China’s legal system. Formal legislation has built a framework for commercial activity and economic investment. Other legislation has helped put in place the necessary infrastructure for a market economy, including the regulation of basic industries and the protection of intellectual property rights. A series of legal reforms has led to a reconstruction of China’s judicial system, and courts have increasingly become forums in which rights created by legislation are vindicated. Animating all of these exciting developments is a commitment to the Rule of Law as a fundamental means of assuring basic justice for citizens and foreigners alike.
Broadly speaking, the Rule of Law requires that legal rules be publicly known, consistently enforced, and even-handedly applied. Aristotle believed the Rule of Law to be “nothing less than the rule of reason,” balanced by considerations of equity so that just results may be achieved in particular cases.• Various approaches can be taken to securing the Rule of Law, and there is no right answer as to which way is best. One thing seems clear, though, and that is the importance of a strong judiciary in achieving and maintaining the Rule of Law. As Woodrow Wilson wrote, government “keeps its promises, or does not keep them, in its courts. For the individual, therefore, who stands at the centre of every definition of liberty, the struggle for constitutional government is a struggle
Foreword to ASIL Handbook for Judges
This overview of international law should provide much-needed background in an area of the law that is rapidly emerging in ways that affect courts here and abroad. The reason for the expanded focus on international law, of course, is globalization. No institution of government can afford now to ignore the rest of the world. The importance of globalization should not be underestimated. Thirty percent of our gross domestic product is internationally derived. We operate today under a large array of international agreements and organizations: the UN Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods, NAFTA, the World Trade Organization, the Hague Conventions on Collection of Evidence Abroad and on Service of Process, and the New York Convention on Enforcement of Arbitral Awards, to mention only a few. But globalization is much more than simply these agreements and organizations. Globalization also represents a greater awareness of, and access to, peoples and places far different from our own. The fates of nations are more closely intertwined than ever before, and we are more acutely aware of the connections. As we learned in this country on September 11, 2001, these connections can sometimes be devastating rather than constructive. But as we also are learning in the post-September 11 world, the power of international cooperation and international under standing is much greater than the obstacles we face.
The word “globalization” has many connotations, some positive and
Speech at dedication of Sandra Day O’Connor High School in Phoenix, Arizona
Student Sandra Day O’Connor Associate Justice was born in El Paso, Texas, March 26 1930. She married John D. O’Connor III in 1952 and has three sons, Scott, Bryan, and Jay. She received her BA and LLB from Stanford University. She served as deputy county attorney of San Mateo County, California for 1952-53 and as a civilian attorney for Quartermaster market center in Frankfurt, Germany, from 1954 through 57. From 1958 through 60. She practiced law in Maryvale, Arizona and served as Assistant Attorney General of Arizona from 1965 to 69. She was appointed to the Arizona State Senate in 1969 and was subsequently reelected to two two-year terms. In 1975, she was elected judge of the Maricopa County Superior Court and served until 1979 when she was appointed to the Arizona Court of Appeals. President Reagan nominated her as an Associate Justice at the Supreme Court, and she took her seat on September 25, 1981. It’s my pleasure to introduce to you, Justice Sandra Day O’Connor. Sandra Day O’Connor All right. Thank you so much. Thank you. This is a really special day for me. Can you imagine driving up to a beautiful new facility like this and seeing your name engraved across the front? It’s quite a thrill. And I can think of no more welcome honor than that which you have bestowed on me to have this beautiful new high school bear my name. I grew up on a cattle ranch in southeastern Arizona. When I was born, my mother wanted to go to a hospital and her parents were living in El Paso.
C-Span interview on The Majesty of the Law
Section on the current court system you say, it has been said that a nation’s laws are an expression of its people’s highest ideals. Regrettably the conduct of lawyers in the united states has sometimes been an expression of the lowest. >> yes. Yes. I have had a concern that has increased through my years as a lawyer with a decline in professionalism in the legal profession. and perhaps in others as well. But that’s the one with which I’m most familiar. and I graduated from law school in 1952, from Stanford law school. And we met in a reunion, perhaps our 40th reunion, I don’t remember exactly when this poll was taken. The questionnaire was sent out to all of us by class members asking a series of questions, including the question, if you had to do it all over again and become a lawyer, would you? Would you do it all over again? A majority of my classmates said no. And that shocked me. But I thought it was indeed a reflection of how the legal profession has changed since I entered it. And it’s more of a business today than it should be. And less of a profession. I really think that lawyers — people who study law, should expect to provide a lifetime of service to other people who need their help. Whether they can get paid for it or not. And that lawyers should be seeking more to serve than to make as much money as possible. With all of the resultant problems. When my husband, for example, first started to practice law, in those days law firms thought it was quite acceptable
Speech on legal careers at Paint Branch High School, Burtonsville, Maryland
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. Now first of all, we have to get everybody seated, ’cause I’m going to be at this for a while there’s a chair there and there’s one over there. Need to there’s another one here. But I’m to work, right. So it’s Law Day today, May 1. May 1 was celebrated in the former Soviet Union as a day to remember the ascendancy of the Communist Party there. And perhaps it was in reaction to that, that we started celebrating May 1 as Law Day in this country. And it’s become a day that we care about, at least in the legal profession we do. And I hope other citizens do too, because it does give us an opportunity to talk about the role of law in our society, the role of courts and a fair judicial system. And that’s what I’m involved in, in my work today. And it didn’t start out that way. I was told you might like to know how I started out. I grew up on a cattle ranch in the dry, arid Southwest, it was half in Arizona and half a New Mexico we straddle the state line. And the ranch was quite remote we were 35 miles from and it was a life built around the small group of people who ran the ranch my parents and the people who were there. And we were not many in numbers. And the people who work there, the Cowboys tended to be single man who spent their whole lives there. We had at least four who stayed until their ultimate death as old man and spent respectively something like 70 years, they’re over 50 in three other cases.
So it was a small knit group that tried to
“Sandra Day O’Connor’s Supreme Legacy”
NPR Host for 191 years, this nation’s highest court was a men’s only club. In 1981. Sandra Day O’Connor broke the gender barrier. But when she decided to write her first book, it wasn’t about the court but about her childhood growing up as a cowgirl on the Lazy B ranch in Arizona, are now in a new book. She writes about the institution where she’s lived for the last 22 years the Supreme Court. Yesterday, Justice O’Connor sat down with NPR legal affairs correspondent Nina Totenberg to talk about her latest work entitled the majesty of the law. Nina Totenberg Sandra Day O’Connor was not exactly a household name in 1981, a mid level appeals court state judge who had previously served in the Arizona Senate. She was by her own account, not exactly nationally recognized for her scholarship or judicial writing. So she didn’t take it very seriously one day in 1981, when she got a call from the Attorney General of the United States, asking her to come to Washington, DC See to discuss a vacancy on the US Supreme Court. Sandra Day O’Connor I wasn’t genuinely excited about the prospect of me being on the court because I didn’t think I would be. Nina Totenberg Do you think it was an affirmative act? A good affirmative act, but Sandra Day O’Connor an affirmative act? Well, certainly the president reached out to decide, I want to appoint a qualified woman to the court and I’m going to do it if I have the chance. And he did. That was out of the ordinary. Nina Totenberg But he had to look
PBS interview discussing her book, The Majesty of the Law
Unknown Speaker In 1981, Sandra Day O’Connor made history, she became the first woman to serve on the Supreme Court. But that honor is actually one milestone in a long and accomplished career dedicated to the law. In 2003, Justice O’Connor talked about her work and life with NBC correspondent Pete Williams. taped in front of a live audience at the Kentucky Center for the Arts, great conversations, just to Sandra Day O’Connor and Pete Williams. Pete Williams And then we begin with a passage that’s in both of your books the lazy be and the majesty of the law. It’s from one of your professors at Stanford, the great novelist, historian and biographer Wallace Stegner, you know the passage I’m referring to would you read that to us Sandra Day O’Connor Right now let me find out I should have marked all this. Yes, here it is. Wallace Stegner was my favorite American author still is but he’s passed away. And this is what he wrote, among other things about the West. You know, he grew up in Saskatchewan, Canada, and then moved to the west and he loved the West. He said, There is something about living in big empty space where people are few and distant, under a great sky that is alternately serene and furious. exposed to son from four in the morning till nine at night, and to a wind that never seems to rest. There is something about exposure to that big country that not only tells an individual how small he is, but steadily tells him who he is. Pete Williams When you grew up in just
Acceptance speech for receiving Honorary Doctor of Laws from The George Washington University
JUSTICE O’CONNOR: Thank you, thank you. President Trachtenberg, Dean Young, faculty, graduates, and friends of George Washington University School of Law:
It’s a great pleasure to be with you today at this ceremony. After all, it’s a day of joy for everyone. You graduates have no more law school exams or classes to endure — (Applause.) — and I might say the faculty no longer has you to endure. You have fame and fortune ahead of you. Your families and spouses and friends can look forward to seeing more of you, and your speaker is greatly honored by the honorary degree bestowed on her today, a degree which allows me, like you graduates, to always have a link with this great Law School.
I realize we’ve gathered here today to applaud those of you who will be receiving law degrees. There are, however, several heroes and heroines here who should be recognized and with whom you graduates undoubtedly would like to share your glory. I refer, of course, to the parents and perhaps spouses who’ve made two significant contributions to your presence today, your parents have anyway. First, they had the brains which you were lucky enough to inherit; and secondly, they probably provided at least some of the money you needed to sustain yourselves while you were here.
I congratulate your parents and I commend you graduates for your good judgment in selecting them. (applause.)
A commencement speech is a particularly difficult assignment. The speaker is given no topic and is expected
Speech at groundbreaking ceremony for the modernization of the Supreme Court building
William Rehnquist Good afternoon. It’s my pleasure to welcome you to the groundbreaking ceremony for the modernization of the Supreme Court building 72 years ago in the spring of 1931, the work of digging the foundation for our beautiful building began. Four years later, on April 4 1935, the building was completed. The total cost, including furnishings was less than $10 million. And it came in under budget, with almost $100,000 returned to the Treasury. The runner vision project for which we break ground today is scheduled to take five years, and it cost 120 $2 million. when it’s completed, I hope that we will again be returning funds to the Treasury, but I’m not betting on it. William Howard Taft, who served as Chief Justice from 1921 to 1930, was the moving force behind constructing a separate building for the court. Although he did not live long enough to see it completed. Until this building open, the court did not have a home of its own. From 1800 and one until 1935. It occupied cramped quarters across the street in the capital, very much at the sufferance of Congress. And most justices worked out of their homes. having its own building was a great symbolic importance to the court. The building has been Captain excellent repair, and looks as beautiful today as when I first saw it, February of 1952. But after nearly 70 years, it’s overdue for renovation. I would like to thank the members of the courts building committee, particularly Justice O’Connor, who chairs the committee,
Speech at the opening of the National Constitution Center
John Street Ladies and gentlemen, please join me in honoring the 2003 recipient of the Philadelphia Liberty metal. United States Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day. Oh, Sandra Day O’Connor, a great American who has demonstrated leadership and vision and carriage in the pursuit of liberty. John Street Justice O’Connor, we are proud to welcome you to our city, and our Sunoco, welcome America celebration. We are particularly pleased to present you with the Philadelphia Liberty medal on this awesome and historic location, the opening of this spectacular National Constitution Center. Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you, Mayor Street and thank all of you here today for joining in this absolutely wonderful occasion, as we celebrate both our nation’s birthday and the opening of the National Constitution Center here in the great city of Philadelphia.
The Constitution Center and independent Hall, together with the Liberty Bell, form a place that every American should visit. It will contribute each and every day to the reinforcement of the basic principles that bind us together as a nation and a people. And Joe Torsella, thank you so much for your perseverance, and for reminding us today that even supreme court justices make mistakes.
On May 25, 1787, here in Philadelphia, a quorum of delegates from seven states met in answer to the call from the Annapolis Convention to draft what became the Constitution of the United States. The delegates unanimously selected George Washington as president
Speech on women in the law to the Philadelphia Bar Association
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you, Audrey, Kelly, for your wonderful presentations today. And what a delight it is for me to be here when you receive the Sandra Day O’Connor award that you participated and establishing 10 years ago. It’s great and to be and to be present. When so many of the previous Sandra Day O’Connor award winners could be here. And what a wonderful group have been selected. The Philadelphia Bar Association has been particularly kind to the female division of the United States Supreme Court. I’m truly delighted that you’ve established now an annual justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg legal writing award, it is exceedingly appropriate because Justice Ginsburg rights with a very, and I careful and no one among us doesn’t matter. So it’s a real special treat to be here today with Justice Ginsburg, as that effort is launched. And on hand, usually at your special events in Philadelphia is judge Norma Schapiro over here at the table today, whose career here in Philadelphia has spanned more than five remarkable decades. She has said that one of her favorite quotations is from the ancient Roman official Gaius who poignantly noted that one who helps the wandering traveler does as it were, light another’s lamp by their own, and it gives no less light because it helped another. And as the first woman appointed to the United States District Court of the Eastern District of Pennsylvania, her live show in dark corners where women never before had traveled. And she has led her light
Speech to the Southern Center for International Studies
President White, Judge Dorothy Beasley, Secretary Sullivan and friends of the Southern Center for International Studies. The impressions we create in this world are important and can leave their mark. A friend of mine tells the story of a bus driver who was becoming angry but still kept his composure when a woman passenger made many complaints during the trip. She was rude and made the trip very unpleasant for those around her. It wasn’t until the driver opened the door at her stop to let her off the bus that the driver said, “Lady, you left something behind.” She turned and snarled, “And what was it I left behind?” The driver smiled and said softly, “A bad impression.”
On the whole, the United States judicial system leaves a favorable impression around the world. But when it comes to the impression created by the treatment of foreign and international law in United States courts, the jury is still out. A skeptic of the relevance of non-U. S. law to the United States legal system would begin by asking why judges and lawyers should divert their attention from the intricacies of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act, or the Americans with Disabilities Act, or the Bankruptcy Code, to the principles and decisions of foreign and international law.
The reason, of course, is globalization. No institution of government can afford any longer to ignore the rest of the world. One-third of our gross domestic product is internationally derived. We operate today under a large array
Dedication: Lending Light to Countless Lamps: A Tribute to Judge Norma Levy Shapiro
DEDICATION
LENDING LIGHT TO COUNTLESS LAMPS:
A TRIBUTE TO JUDGE NORMA LEW SHAPIRO
SANDRA DAY O’CONNORt
There is a sad but common misconception in our society that time and energy contributed to others is time and energy lost. Rare is the individual with the perspective to recognize that we may give without losing, and that it is often in giving that we gain.
Judge Norma Shapiro is such an individual. In a career that has spanned more than five remarkable decades, Judge Shapiro has dem onstrated a sincere selflessness that is immeasurable in its impact. She has said that one of her favorite quotations is from the ancient Roman official Gains, who poignantly noted that “[o]ne who helps the wan dering traveler does, as it were, light another’s lamp by their own, and it gives no less light because it helped another.”1 And indeed, as we pay tribute to her extraordinary professional and personal accom plishments, we cannot help but recognize the countless lamps to which she has lent her light.
When she began law school in 1948, Judge Shapiro was one of only eight women in her class at the University of Pennsylvania. As one whose timing and experience was parallel, I can say with some confidence that this path sometimes was not easy. Nonetheless,Judge Shapiro thrived. She served as an editor of the Law Reviewand gradu ated at the top of her class. And in the years that followed, women who walked the same path into that predominantly male world knew that they could count on her
Discussion with the Council for Excellence in Government
Pat McGinnis Good morning, and welcome. I’m Pat McGinnis, President and CEO. The Council for excellence in government. And today actually at a luncheon immediately following this discussion, we will present the Elliot Richardson Award for Excellence in public service to two outstanding public pioneers. Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O’Connor and Secretary of Transportation, norm moneta, and we are so delighted to have them with us this morning. This award is named in honor of Elliot Richardson, who was well known to everyone in this room, I think, as a giant public servant, the only person to have led for cabinet departments and a decorated hero in World War Two, not to mention lots of other amazing accomplishments on his resume. And Elliot would have absolutely loved the celebration of excellent public pioneers whose radical moderation like his has led to amazing accomplishments, not only for government but for the whole society. Shortly after Elliot died on New Year’s Eve 1999, the council for excellence in government established announced the establishment of this prize to honor his legacy of imagination, courage and leadership. The idea is to recognize extraordinary public servants, who are role models for a new generation of public pioneers. And in our view, what better way to inspire young people to come into public service than to tell stories inspirational personal, true stories, of unusual journeys, of overcoming obstacles of commitment and determination with A little
Professionalism: The Commitment and Dedication to Making a Difference
IT IS HARDLY A SECRET THAT MANY LAWYERS TODAY ARE dissatisfied with their professional lives. The pressures associated with the increasing commercialization of law practice have made lawyers, as a group, a profoundly unhappy lot. As one New York Times article concluded: “Job dissatisfaction among lawyers is widespread, profound and growing worse.”1
An examination of the research on lawyers’ overall well-being isdeeply troubling. Attorneys are more than three times as likely as nonlawyers to suffer from depression, and they are significantly more apt to develop a drug dependency, to get divorced, or to contemplate suicide. Lawyers suffer from stress-related diseases, such as ulcers, coronary artery disease, and hypertension, at rates well above average . Unsurprisingly, a recent RAND Institute study of lawyers in California found that they were “profoundly pessimistic about the state of the legal profession and its future” and that only half would choose to become lawyers if they had it to do over.2
This dissatisfaction with the present state of the legal profession is not limited to those within the legal community. Lawyers increasingly have been the subject of public derision. A lawyer in Texas recently filed a lawsuit claiming that he had been the victim of housing discrimination. Apparently, after several unpleasant experiences, the property company had adopted a policy of never selling new homes to attorneys. In economics, lawyers are typically described as creating deadweight
The Majesty of the Law: Reflections of a Supreme Court Justice
Acceptance speech for the Center for the Study of the Presidency’s Publius Award
Host If our guest of honor has often defied the odds, so too, she has resisted those who would put a label on her judicial philosophy for labels for cans, not coalition builders. for 23 years, she has demonstrated a rugged individualism reminiscent of the Arizona frontier of her girlhood belonging to no quick or ideological camp, as committed to the separation of powers as Publius as suspicious of judge made war as homes. officiating at a wedding in 1931. Justice Benjamin Cardozo’s spoke of quote, three grades mysteries in the lives of mortal beings, the mystery of birth at the beginning, the mystery of death at the end, and greater than either the mystery of love. Everything that is most precious in life is a form of love. Art is a form of love, if it be Noble. Labor is a form of love, if it be worthy. Thought is a form of love, it be inspired the art of jurisprudence, the labor of legal interpretation, the thought of a lifetime devoted to justice in the spirit of Cardozo, and the tradition of homes. It is no mystery by the Center for the Study of the presidency, should present the 2004 police award to Justice Sandra Day O’Connor, whose wall the wall is inseparable from her passion for justice. Congratulations. Sandra Day O’Connor That was quite an introduction. I wish the Cowboys could have heard that. Back at the lazy BR Richard Norton Smith is a wonderful historian and john and i were first privileged to meet him at the Ronald Reagan library. And it’s fun to hear him speak
Bridge to Public Service. It’s Up to Civil Servants to Tell Young People About the Great Opportunity to Change Lives and the Nation
Advice+Dissent
VIEWPOINT
Bridge to Public Service
It’s up to civil servants to tell young people about the great opportunity to change lives and the nation.
The following are excerpts from a speech by U.S. Supreme Court Justice Sandra Day O’Connor in her acceptance of the Elliot Richardson Prize from the Council for Excellence in Government in March.
Elliot Richardson, former U.S. attorney general, knew that ours is a nation built on pride in sacrifice and commitment to shared values-on a willingness of its cit izens to give of their time and energy for the good of the whole. He knew that there is no greater contribution than a life of dedication to public service. We are the nation that we are today because those bridge builders of the past gave of themselves in a way that really mattered.
To be sure, the work of bridge building can be as taxing as it is rewarding. These efforts can call for sacrifice-sometimes emotional, sometimes finan cial, sometimes personal. Those who choose the life of public service open themselves to public review.
Sometimes, I’m sorry to report, the nation that we aim to serve is not content with our efforts. But the ever-present understanding that you are a part of something bigger than yourself, and that your efforts are paving the way for those who will follow, makes a life of public service worth the bumps along the way. We cannot expect that a single gen eration of public servants will be able to bridge the gaps of inequality and injustice.
Interview on 60 Minutes
Justice O’Connor
produced by
Bill Owens
Catherine Herrick
Scott Pelley Of all you’ve heard about Ronald Reagan, there is someone you haven’t heard from. A person who has had almost as much impact on the history of our nation as the president himself. As a rule, Supreme Court justices don’t give many interviews. But Justice Sandra Day O’Connor sat down with us to talk about the man who made her the the first woman on the Supreme Court. Since that day in 1981, Justice O’Connor has become one of the most powerful women in America. In the years since Reagan left office, O’Connor has been the deciding vote, laying down the law of the land on abortion, affirmative action and the decision that made George Bush, President of the United States. We sat down with Justice O’Connor at the Supreme Court, an institution that had seen only men on the bench for nearly two centuries until Ronald Reagan changed it forever.
Sandra Day O’Connor It had an incredible ripple effect, of making opportunities become available for women. It was, it was just a remarkable transformation. And I really think he deserves an enormous amount of credit for making that happen in this country.
Ronald Reagan I will send to the Senate, the nomination of Judge Sandra Day O’Connor, of Arizona Court of Appeals, for confirmation as an associate justice of the United States Supreme Court.
Scott Pelley Just six months in office, President Reagan made his first appointment to the court. And other than his work to end
Remarks at funeral of President Ronald Reagan
This is a reading from a sermon delivered in 1630 by the Pilgrim leader, John Winthrop, who was aboard the ship The Arabella on his way from England to the Massachusetts Bay colony. The city on the hill passage was referenced by President Reagan in several notable speeches.
Now, the only way to provide for our posterity is to follow the council of Micah, to do justly, to walk humbly with our god. We must delight in each other. Make others’ conditions our own, rejoice together. Mourn together. Labor and suffer together. Always having before our eyes our commission and community in the work as members of the same body. The Lord will be our God, and delight to dwell among us as his own people. For we must consider that we shall be as a city upon a hill. The eyes of all people are upon us. So that if we shall deal falsely with our God in this work we have undertaken, and so cause him to withdraw his present help from us, we shall be made a story and a byword through the world.
Acceptance speech for the American Institute for Public Service’s Jefferson Award
Unknown Speaker Thank you very much. Now, Justice Sandra Day O’Connor. In June, she received the Jefferson award by the American Institute for Public Service. In 1972, Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis was one of three founders of the Institute, which called their Jefferson awards, a Nobel Prize for public and community service. Justice O’Connor was introduced by Charles Bartlett, the friend of the Kennedy family. Unknown Speaker I take great pleasure being given the honor of making this award, the greatest public service by an elected or appointed official, because in all years, we’ve been giving this award and are now quite a number of those years. I can never remember an award. When that was more appropriate than this one. I feel very strongly I come to this podium with great gusto. Because I think that Sandra Day O’Connor and her husband have brought to this town, a spirit that didn’t have before a liveliness, and a sense of participation, which is really invigorated this capital had been very important to us in worship. Unknown Speaker She gave us a little of her background and a very good sense that she’s actually romanticized her background in a marvelous book, which I hope all of you will read called lazy be lazy business story of her young life on this ranch, and beautiful part of the West. And in this book, we sort of feel that she got a special learning experience from a black cow hand name rosters. She describes him as a man without schooling, but a master on the range,
Commencement speech at Stanford University
President Hennessy, faculty, graduates and friends of Leland Stanford Jr. University: It is a great pleasure to be with you today at your commencement exercises. After all, it is a day of joy for everyone: You graduates have no more exams or classes to endure. And I might say, the faculty no longer has you to endure; you have fame and fortune ahead of you; your families and spouses and friends can look forward to seeing more of you; and your speaker is greatly honored by the privilege of being with you today as a speaker at your commencement.
I realize we have gathered here today to applaud those of you who will be receiving degrees. I suggest, however, that there are several heroes and heroines here today who should be recognized and with whom you graduates would like to share your glory. I refer, of course, to the parents, who have made two significant contributions to your presence today. First, they had the brains that you were lucky enough to inherit and, secondly, they probably provided at least some of the money you needed to sustain yourselves while you were here. I congratulate your parents, and I commend you graduates for your good judgment in selecting them.
A commencement speech is a particularly difficult assignment. The speaker is given no topic and is expected to be able to inspire all the graduates with a stirring speech about nothing at all. I suppose that’s why so many lawyers are asked to be commencement speakers; they’?re in the habit of talking extensively
Speech at the Chautaqua Institution
Sandra Day O’Connor
Thank you, Tom. And what a pleasure it is to be back here at Chautaqua. This such a special place, tucked under Lake Erie and along our border with Canada. The United States has only two next-door neighbors, Canada, and Mexico. I lived most of my life closer to the Mexican side of our border. I was born in El Paso, Texas and grew up on a ranch. And it was mostly in Arizona, and partly in New Mexico. And it’s a far cry from the shores of Lake Erie and Lake Chautaqua to that dry, semi-arid desert where I spent my early years.
When I first moved from Arizona to Washington, DC, John and I lived in an apartment in the Watergate that was kindly secured for us by my colleague Justice Lewis Powell as a temporary residence. We could look out our window, a view of a splendid statue of President Benito Juarez of Mexico, the former president. It’s inscribed with his words, “Respect for the rights of others is peace.” President Juarez has a place in Mexico’s pantheon of heroes, just as President Abraham Lincoln has in ours.
I thought of these two men as I reviewed one of the themes you’ve been considering this week, that human progress and human violence have been linked historical forces. In the 1860s, both these leaders, Juarez and Lincoln, led their countries out of violence and deadly conflict. Mexico faced a threat from outside in the form of the French intervention led by Napoleon [III]. The United States faced a threat from within. Now, having led their young
Speech at dedication of Eric E. Hotung Building at Georgetown University
DEDICATION OF THE ERIC E. HOTUNG INTERNATIONAL LAW CENTER BUILDING: KEYNOTE ADDRESS
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR*
This is a very happy occasion indeed. And I’m glad that as a neighbor I was invited to come over and share this day with you. Georgetown University Law Center is our nation’s largest law school. It is consolidat ing its broad international law programs under one roof in the new Eric E. Hotung International Law building. This law school, which is located in our nation’s capital, already has one of the most comprehen sive international and comparative law programs in the world. It has at least twenty-two talented faculty members focused on these areas. Students from at least seventy-one countries are enrolled here in the international programs. Alumni of this law school live all across the globe, and the law school is already home to many diverse programs in the international area. In short, Georgetown University Law Center is now situated to be the leading global law center in this country and perhaps in the world. No wonder this is a special day.
International law has emerged in ways that affect all courts here and abroad. The reason is globalization. Its importance should not be underestimated. Thirty percent or more of our gross domestic product is internationally derived. We operate today under a very large array of international agreements, treaties, and organizations: the United Na tions Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods, the North American
Speech on the relationship of international law to the U.S. Supreme Court at Georgetown University
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you Dean Atlanta so much. Thank you. Thank you. His Eminence Cardinal McCarrick, President there, joi de Dana Lana cough and Dean Emeritus Judy or bream, and faculty, students and friends of Georgetown University Law Center. This is a very happy occasion indeed. And I’m glad that as a neighbor, I was invited to come over and share this day with you. Georgetown University Law Center is our nation’s largest law school. consolidating its broad and international law programs under one roof in the new Eric EO tongue, international law building the generosity of ambassador and Mrs. How tongue has made this possible. This law school, which is located in our nation’s capital, already has one of the most comprehensive international and comparative law programs in the world. It has at least 22 talented faculty members focused on these areas. Students from at least 71 countries are enrolled here in the International Programs. alumni of this law school live all across the globe. And as you’ve heard from the dean, the law school is already home to many many diverse programs in the international area, in short, Georgia. University Law Center is now situated to be the leading global Law Center in this country and perhaps in the world. No wonder this is a special day. International Law has emerged in ways that affect all courts here and abroad. The reason is globalization. It’s important should not be underestimated. 30% or more of our gross domestic product is internationa
Speech on jury service reform to the American Bar Association
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you, President Gray. I appreciate that so much. And thanks for letting me be part of the effort today. I think my interest in this came about because of my years as a trial court judge and dealing with jurors in a great mini criminal as well as civil cases. And the jury system in this country is one of the most enduring aspects of our legal system as a whole. And the only time that most Americans other than lawyers and letting them see the inside of an actual courtroom is when they’re called to serve as jurors and juries have a proud history in this country as well as in England, where the jury as we know, developed today, Great Britain, Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the United States. Continue to use juries to hear evidence and determine facts. In a great many criminal cases. All only the United States and New Zealand continue to require use of juries in most civil cases. So it’s a shrinking universe out there. The Russian Federation is experimenting with the use of juries in serious criminal cases. And that seems to be expanding now to all parts of the Russian Federation. I think juries usually their do their jobs very well and occasionally show extraordinary courage in the face of hostile judges, perhaps, and try to deliver the verdict that justice demands, even if it might not be the one that the judge might want. I presided over many a trial and in all but two or three cases, I felt that the jury reached an entirely Appropriate verdict. And
Conversation with Justice Stephen Breyer
NARRATOR: In the summer of 1787, delegates to the Constitutional Convention gathered in Philadelphia to create a document that would establish the government of the United States. On September 17th, that landmark document, our Constitution, was signed. In commemoration of that day, students from several Philadelphia high schools were recently invited to the Supreme Court Building in Washington, DC to meet with Justices Sandra Day O’Connor and Stephen Breyer. The views of the students and the responses of the Justices provided a unique glimpse into the workings of America’s highest court and the document that shaped our history and guides our future. JUSTICE SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR: It’s nice to have you safely here and assembled. And are you all ready to start with some questions about our Constitution and our system? Who’s going to start off? STUDENT: How do you believe the Constitution should be taught in schools, especially with all the new resources that we have, and the fact that a lot of young people simply view the Constitution as something that was created 200-something years ago and is old and maybe out of date? JUSTICE O’CONNOR: I hope that the Constitution is something that every school in America will try to teach to young people. You don’t inherit it through the gene pool. Every generation has to learn about this, learn about the history. Why was it written, why do we have one? What does it provide? What are the benefits of having such a Constitution? Has it worked and
Conversation with students on the 4th Amendment
Unknown Speaker Good evening, Justice O’Connor. My name is Jordan speed and I’m from Wichita, Kansas. How does the Supreme Court decide when a search and seizure is unreasonable? And when it is reasonable? Sandra Day O’Connor Well, it’s a vague sort of a standard issue well know what’s reasonable depends very often on the circumstances in their particular case, the Supreme Court, in effect, has determined that if a search of a suspect is unreasonable under constitutional standards, then the evidence cannot be admitted against that person in any criminal proceeding against the person. Now, you know, many countries around the world don’t follow an exclusionary rule that’s called an exclusionary rule where you can exclude that evidence from any trial proceeding against the person that the state is trying to prosecute. And that’s rather a dramatic limitation on evidence that can be used by this state against someone. And many countries don’t do that. So great britain did, and the United States system map and I guess, Australia to a degree and other common law countries from the British system, but not everybody in the world. Thanks. That’s a good system. But we do and we have this exclusionary rule. So deciding whether a particular search or a seizure of some kind of evidence to use against someone in a criminal proceeding requires judges at the end of the day to make a determination whether that particular seizure or search was reasonable. Well, what’s reasonable? You have arguments
Music and the Law
[A]n overspeaking judge is no well-tuned cymbal.
-Francis Bacon, The Essay on Judicature
As you know, I’ve made a life in the law. And I’ve always loved music, from childhood on.
Lawyers feature in plenty of operas, of course. It starts with Moses, the first Lawgiver, in Rossini’s Mose and Arnold Schoenberg’s Moses und Aron. As expected, Moses generally comes off as an admirable character. But operatic evaluations of later lawyers are more critical. What we find in opera concerning lawyers after Moses is Puccini’s opera Gianni Schicchi about forging a will; a lawyer in Gershwin’s Porgy and Bess who sells Bess a divorce for a dollar-when he learns Bess was never actually married, he raises the price of the “divorce” to $1.50; we also see the lawyer in Strauss’ Die Fledermaus,who is so incompetent that he gets his client’s sentences increased.
The law’s presence is also palpable in the many operas which take place in jails. Jails must be irresistible to composers looking for a place to set a reflective aria-there is plenty of time to think in jail; there is nothing better to do; and the resonance is good. There are jail scenes in Faust, Don Carlo, and Tosca, for instance. Fideliot akes place entirely in jail, portraying a disguised woman’s successful attempt to save her wrongly imprisoned and soon-to-be-executed husband.
Gilbert and Sullivan also come through, as usual, with well placed pokes at the law. In Trial by fury,we meet a lonely Lord Chancellor whose job of approving
Acceptance speech for Harry S Truman Good Neighbor Award
Host Like President Truman, you can call her a liberal on some issues, and you can call her a conservative on others. However, it is clear that she has enabled the High Court to continue its role in the racial integration of our society, and the recognition of gender equality, and in protection of fundamental rights of expression, political participation, and due process of law. And therefore, Justice O’Connor, it is my pleasure to award you the 2005 Harry Truman Good Neighbor award. Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you so much indeed. This is an award that means a great deal to me. It’s a wonderful experience to be here as the recipient of the Harry Good Neighbor award. I have on my desk at the court, a little wooden piece that I bought at the Truman library, when I first visited it when Mr. celebre senior over here was was heading that and it says the buck stops here. And I have proudly had that at my desk as President Harry Truman developed it and had it and he is and President Truman. His reputation, and his legacy has only grown and strengthened with the passage of time. He liked to say he did his best and he did his best throughout his seven years as president from 1945 to 1952. He had to preside over an apprehensive a nation in the midst of a tumultuous world. Soon after, he took over as president World War Two and with the surrender of Germany and 45. the surrender of Japan later at that same year, when the Soviet Union began expanding communist regimes in Eastern Europe and
Speech at University of Houston Law Center
Excerpt quoted in “Afterword, Lazy B and the Nation’s Court: Pragmatism in the Service of Principle”:
[W]hen I entered law school, I didn’t even think about the future, whether I would want to practice law, and if I did, what the job opportunities would be. I just assumed I would be able to get a job, and that was a very naive position, looking back.
I finally called an undergraduate woman friend of mine at Stanford, whose father was a partner in a well-known, very large California law firm, headquartered in Los Angeles. I said, “Ask your father, if you would, if he could get me a job interview in the law firm.”
She did. And he did.
I made the trip to Los Angeles. I sat down with the law firm partner doing job interviews, and we chatted for a little while, and then he said, “Ms. Day, how do you type?”
I said, “Well, medium. I can get by but it’s not great.”
He said, “If you can demonstrate that you can type well enough, I might be able to get you a job in this firm as a legal secretary. But Ms. Day, we have never hired a woman as a lawyer here, and I don’t see the time when we will.”
So that was pretty much the situation.
Discussion with Justices Stephen Breyer and Antonin Scalia, moderated by Tim Russert, at the National Archives
MR. RUSSERT
Justice O’Connor, what should the American people know about our Constitution?
JUSTICE O’CONNOR
It’s unfortunate today, Tim, as you learned the other night, that young people in our country are growing up without any classes in civics, most of them without any knowledge or understanding of the Constitution or what’s in it and what it protects for our citizens.
JUSTICE O’CONNOR
And this is a major problem for our country, because you don’t inherit the knowledge through the gene pool. You have to learn it. Each generation has to learn it. And I think our goal ought to be, with young people, to give them the basics of what’s in that.
JUSTICE O’CONNOR
When I travel around the world, I guess the thing that I have come to respect the most is our Constitution and our legal system in this country, which gives you a certain feeling of confidence in this country that I don’t see elsewhere in the world.
MR. RUSSERT
Justice Scalia, what should the American people know about our Constitution?
JUSTICE SCALIA
I have a talk that I give to young people now and then about the Constitution. And it begins by trying to make them realize that it is something — a Constitution is of unique importance to Americans, for a number of reasons.
JUSTICE SCALIA
For one thing, Americans are an odd society. I’m not sure one like this ever existed before. Martin Diamond, the political scientist at Georgetown, since deceased, once observed that there is no word in a foreign language equivalent
Remarks on retirement from the Supreme Court at the Ninth Circuit Judicial Conference
Host And that is very high praise from him. Maybe growing up in the arid West now draws you to its waters. In appreciation for all that you have done for us and for the nation. We offer you a small token of appreciation and hope that the waters of the West will bring you back to us in the years to come. Justice O’Connor, thank you. And our, the gift is a fly box, inscribed, “Presented to Justice Sandra Day O’Connor, with appreciation, from your friends in the Ninth Circuit, July 21, 2005.”
Sandra Day O’Connor But what’s in it? Aha. All right. Now this looks like some serious fishing flies that I will very much enjoy trying to put to use with better luck than I had on Tuesday. And it’s a perfectly wonderful box and the flies look great. And I can’t imagine a better thing for you to leave with me to tempt me to come back many times. Ninth Circuit territory. Host Thank you judge–
Sandra Day O’Connor Now they’re gonna make me go to work. Host Thank you, Judge levy. Justice O’Connor. Your announcement took us all by surprise. Was it a difficult decision for you? Sandra Day O’Connor Yes. Yes. It’s been such a privilege to serve on the Supreme Court. When I was little, I always wanted to work. I wanted to work at some kind of work worth doing. Something where the individual effort put in would make a difference. And I was so privileged to serve 24 years at work that fitted that category very well. And then some. So I was lucky to have it. Host Judge Marilyn huff who was the former
Chico
Speech at Scottsdale Public Library on her book, Chico
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you. That’s a great idea. I don’t know what could matter more in a community than the library. As all of you probably already know I grew up on a ranch in a very remote part of Arizona, half of the ranch was in New Mexico. The ranch straddled the state line. But the house was physically in Arizona. Most of the road from the highway was in New Mexico. But then it circled back into Arizona and that’s where I grew up. We were between Duncan, Arizona, and Lordsburg, New Mexico. About 30 miles from town either way. We didn’t go to town often in those days, and the ranch was sparse and dry. You know what the Arizona high desert country is like. And it’s full of everything that has teeth or claws or sharp spines — something to hurt you. And you learned early on to be a little bit careful about where you stepped and walked and rode and how you handled things. That can stand you in good stead through life, I think, is you have to walk through the bramble bushes of life. But my friends in my early years were books. I didn’t have siblings until about 10 years after my birth. And my friends were my parents and the cowboys who lived there at the ranch. And books. And I loved to read from early on. It meant so much to me. And that’s why I guess I have an affinity for libraries and why the invitation of the Scottsdale public library was a welcome one. I’ve not had a lot of time to write just for the sake of writing.
My bookshelves in my home are lined with something
We Need a Clear Set of Rules to Reaffirm Our Values as a Nation
It is a great privilege and honor to be at West Point today. The beauty and history of this institution make it one of our nation’s most treasured places. To be here and receive the Thayer Award, and to review a Parade is the experience of a lifetime. The previous recipients have most often been people with substantial military experience, such as General Colin Powell, Senator Robert Dole, and General Douglas MacArthur. By comparison, I am merely a sideline observer. Even Bob Hope – who came here to receive the award in 1968 – had more military experience than I do. As a result, West Point is making a bit of an exception in presenting the award to a mere Supreme Court Justice.
I understand that the Thayer award is supposed to be given to an “outstanding citizen of the United States whose service, accomplishments, and stature exemplify personal devotion to the ideals expressed in the West Point motto, “DUTY, HONOR, COUNTRY.” That is a wonderful and grand motto. I have been tested a bit lately on the “duty” front: As many of you know, I did my best to retire from the Supreme Court this summer. The President nominated Judge John Roberts to be my successor, and I assumed I might be trout fishing in Montana or seeing my grandchildren in Arizona on the first Monday of October, when the new term started. Then the nation learned of the sudden death of our Chief Justice, William Rehnquist. He served on the Supreme Court for 33 years in all and was a great Chief Justice. He was also a
Remarks to the American Bar Association on the global rule of law movement
Sandra Day O’Connor
I want to thank the American Bar Association for all of the important work that it does to promote the rule of law and for convening this really important meeting to advance that cause. Now why? It’s because the rule of law offers a basic guarantee of good government, of fair treatment and accountability. And these are the building blocks for a society that can effectively protect its citizens and help them reach their own potential. The discussions held here have underscored the urgency of promoting the rule of law, not just to realize the human potential, but also as part of an effective strategy to address some pressing social problems.
We have some critical challenges: combating terrorism, combating corruption, poverty, and the threat of pandemics. And all of these would be alleviated, in part, by a rule of law movement. But this can’t be a project of just one organization, or one profession, or one country. I think each of us has a stake in the rule of law, and we have to work together toward the goal. No one country has all the answers, certainly our country does not. You’ve learned that in the United States, there are current threats to the independence of our judiciary and the rule of law. And I think there are problems in most countries in that regard. So one of the important contributions that this gathering has made has been bringing together a wide range of different stakeholders in the concept of the rule of law, from the private sector, from
Panel discussion on the role of the judiciary with the American Bar Association
Unknown Speaker Their stories of world war two Korea and Vietnam. Three members Unknown Speaker of the Supreme Court talked about the role of the judiciary at this event hosted by the American Bar Association. justices Stephen Brier, Unknown Speaker Sandra Day O’Connor and Anthony Kennedy spoke for just under an hour and a half. Unknown Speaker As we get in this part of the program, we’re going to vary from oral questions to written questions. So I, as you Stephen Breyer hear the Unknown Speaker presentation and you have your questions, please write them down. And then when we asked for them, you can put your hand up and we’ll pick them up. Justice Kennedy will need to leave slightly early. But and we will miss him but we will continue to there’s the normal time at this time. You already know my great co our president American Bar and he will now introduced this program. Unknown Speaker Good afternoon, everyone. Unknown Speaker We are all in for a treat Unknown Speaker during the next 90 minutes. And while we’re doing the technology here, let me offer it an observation and a question of all of you. The observation is this, I have to leave immediately after this panel to go to the airport. Because tomorrow morning at 8am, I’ll be in Seattle, Washington addressing the judiciary on the way judges are selected in the state of Washington. So I won’t have a chance to speak with you after I leave. My question to you is this after I pay respects to the people who have made this
Remembering Rehnquist
Remembering Rehnquist
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR
William Hubbs Rehnquist spent the last thirty-three years of his life as a member of the U.S. Supreme Court, fifteen as an Associate Justice and eighteen as Chief Justice. I met Bill when I was a freshman at Stanford in 1946. He was attending Stanford and working part time as a “hasher” at my dormitory during the evening meal. He amazed all of the young women by carrying such heavy loads of dishes on his tray. Perhaps that is how he learned to carry all those heavy loads in all of the years that followed. He was tall and good-looking, and he had a sharp sense of humor.
In 1950—after he had graduated Phi Beta Kappa from Stanford with a B.A. and an M.A., and received another M.A. from Harvard—he and I enrolled at Stanford Law School. He really put the “Bill” into the “G.I. Bill”: he had attained the rank of sergeant and had served in the Army Air Corps as a weather observer in the United States and North Africa. Like many of my classmates who had served in the war, he was serious about his studies and eager to get his LL.B. and practice law. Bill was clearly the brightest in our class, always prepared and willing to express his views when asked, and his conservative views were backed up by brilliant analysis. We also enjoyed bridge games, charades, and occasional movies. Little did either of us expect to serve on the Supreme Court one day.
Our class was very excited when Bill got a Supreme Court clerkship with Justice Robert
Acceptance speech for the National Association of Women Judges’ Lifetime Achievement Award
Sandra Day O’Connor Well, President Ruiz that was quite a presentation indeed. And accolades, compliments from one’s peers, my fellow women judges are the ones that are most appreciated, as you know. And I’m just overwhelmed by all the kindness that you have shown tonight in hosting this great reception and expressing in such generous terms. Your appreciation, I remember so well, when Joan Dempsey climb, then a judge in California decided to get this organization going. And I promptly joined, not having any idea at the time that it would grow as it has, perhaps it would not have done so had not President Ronald Reagan decided, I thought rather courageously to put a woman on the Supreme Court. He campaigned, as you pointed out, saying he wouldn’t do it. And his action opens so many doors for women not only in this country but around the world. I remember so well, the day he called me and after I left the interview in his office, I think he did talk to some other people and I left that office and flew back to Arizona that day, and breathed a big sigh of relief. I was interested to obscene the Oval Office and to met with the president and some of his advisors and I said to myself, thank goodness, I don’t have to go to Washington and do that job. I really did not imagine that I would be at I mean, my classmate at Stanford, William Rehnquist, was already a member of the court. And I couldn’t imagine that that would happen. But it did. And I had to take a lot of deep breaths to decide.
Speech at the National Women’s History Month Celebration
MS. KAREN P. TANDY: Good morning. I am the administrator of the Drug Enforcement Administration and it is my honor thank you for being here today and to ask you to please join me in welcoming the Attorney General and Justice O’Connor for today’s event.
I would like to point out to some special people with us this morning, first, Mr. John O’Connor, the husband of Justice O’Connor, and Mrs. Rebecca Gonzales, the wife of the Attorney General.
I ask you now to please rise for the presentation of the Flag by Girl Scout Brownie Troop Number 470 and for the singing of the National Anthem by Ms. Anamer Castrello.
You may be seated. Please join me in thanking these very special young Trail Blazers for the future of women, the Brownie Girl Scouts.
And, Ms. Castrello, thank you. Thank you for that stirring rendition of the National Anthem.
Welcome to all of you today. When I think about our theme, “Women: The Builders of Communities and Dreams,” I cannot help but think about some of those little known women from the American Revolutionary period who made it possible for us to have our communities today because of what they did back then in building our great nation.
The demure hoop-skirted women of the 1700s were the same women who tricked the enemy. The Red Coats met their match when they invaded the home of Mrs. Murray, a woman known only to us as Mrs. Murray, for Mrs. Murray plied the British generals with enough liquor that the small band of American soldiers were able to sneak
“Response” (The Legacy of Chief Justice Rehnquist and Justice O’Connor)
It is not fair to have to follow a speaker as eloquent as Justice Kennedy. And I am not going to try to bend your ears for long. I am very touched by his comments. It was wonderful that you had a chance to hear him talk about our former colleague, William Rehnquist, as well as some remarks about me.
Our Stanford alums have lost two members of the Court who belong to Stanford and who belong to the West. We used to take a lot of pride in how we just needed one more to have a majority on the Court from Stanford. Now I guess the chances of a Court majority from Stanford are not so good. When I started at Stanford Law School back in the Dark Ages, the Law School was in the inner quad. And it was a funny little part of the inner quad–the law library was quite old and musty and we had an owl that lived in the stacks. I used to do homework in that library, and I’d always watch and see where the owl was sitting that day.
Bill Rehnquist was my classmate, and I often sat next to him. I would look over and see what kind of notes he took. I took copious notes. I tried to write down everything the professors had to say. But he ended up each hour with a perfect outline, and he just captured exactly the essence of what was presented. He did a great job. He could have made a fortune on those notes had he chosen to do so.
The Law School then moved into nicer quarters. It was on the outer quad, over near the Business School facing Palm Drive. We thought we were in high cotton when we got there.
“Not By Math Alone”
March 25, 2006
Fierce global competition prompted President Bush to use the State of the Union address to call for better math and science education, where there’s evidence that many schools are falling short.
We should be equally troubled by another shortcoming in American schools: Most young people today simply do not have an adequate understanding of how our government and political system work, and they are thus not well prepared to participate as citizens.
This country has long exemplified democratic practice to the rest of the world. With the attention we are paying to advancing democracy abroad, we ought not neglect it at home.
Two-thirds of 12th-graders scored below “proficient” on the last national civics assessment in 1998, and only 9 percent could list two ways a democracy benefits from citizen participation. Yes, young people remain highly patriotic, and many volunteer in their communities. But most are largely disconnected from current events and issues.
A healthy democracy depends on the participation of citizens, and that participation is learned behavior; it doesn’t just happen. As the 2003 report “The Civic Mission of Schools” noted: “Individuals do not automatically become free and responsible citizens, but must be educated for citizenship.” That means civic learning — educating students for democracy — needs to be on par with other academic subjects.
This is not a new idea. Our first public schools saw education for citizenship as a core part of their
Speech to the Campaign for the Civic Mission of Schools
Host So join me in welcoming the honorable Sandra Day O’Connor. Sandra Day O’Connor Come on. No, no. No. I agreed to be part of this Voluntary Group, as a part of the Advisory Council for this effort, because of my absolute conviction that we have to educate all of our young people on how democracies function. What do we mean when we talk about rule of law? How do citizens have the capacity? And do they have a duty to protect? The pay and how to do it? If we don’t do this, it won’t take more than three or four years before we will have created such a gap in the capacity and willingness of our citizens to be good citizens, that our country will take a major decline. There is no question that we have to do precisely the activity that this effort is all about. We have to teach every succeeding generation of young people what it is ourselves. system of government consists of our works, how they can be part of it, and why they should be part of it.
Now, it isn’t easy to do this. My co-honorary chair here, Governor Romer, runs about the second largest school district in the country. And he knows exactly what the problems are. But you see, this knowledge about how we function in this country isn’t handed down through the gene pool. Every generation has to learn it. And we who are older have to be responsible for teaching. I mean, it’s that simple. But you have to teach it in ways that will engage the students. We have maybe a more sophisticated student group and in my day, where
Interview with Diane Rehm, NPR
Diane Rehm Thanks for joining us, I’m Diane Rehm. when ronald reagan nominated the first woman to the Supreme Court 25 years ago, few imagine that Sandra Day O’Connor would emerge as its most influential member since retiring in January. Justice O’Connor is spoken out forcefully and defensive the courts him as huge digital decisions may anger politicians, but retaliatory threats against judges threatened democracy itself. Joining me in this studio to talk about the role of the courts and her service on the nation’s highest court Justice Sandra Day O’Connor, and throughout the hour, we’ll take your calls your comments, questions 800 for 338850 Send your email to Dr. show@wamu.org. Welcome to you just as how con are so good to see you. Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you, Diane. I’m glad to be here and to see you Thank you. Diane Rehm Tell me how concerned you are about the independent The judicial branch of our government, Sandra Day O’Connor I am concerned. I’ve lived a pretty long time now. And in my lifetime, I don’t believe I’ve seen as many complaints by members of Congress, by state legislators, by other officials, and even by the public, about judges. were hearing statements rather frequently, I think, complaining that judges are activists, godless, secular humanists trying to impose some new regime on the nation. And I just don’t see it that way. I understand that. Sometimes judges have to resolve very controversial issues. Sometimes in cases where the good arguments can
Fair and Independent Courts
Sandra Day O’Connor, a Fellow of the American Academy since 2007, served as an Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court from 1981 until her retirement in 2006. The first woman to serve on the Court, she is the author of ”The Majesty of the Law: Reflections of a Supreme Court Justice” (with Craig Joyce, 2003 ) and ” Lazy B: Growing Up on a Cattle Ranch in the American South west” (with H. Alan Day, 2002).
© 2008 by the American Academy of Arts & Sciences
More than one hundred years ago Roscoe Pound delivered an important address to the American Bar Association called “The Causes of Popular Dis satisfaction with the Administration of Justice.”1 In that address, Pound, who would later become dean of the Harvard Law School, warned his audience, “[W]e must not be deceived… into overlook ing or underrating the real and serious dissatisfaction with courts and lack of respect for the law, which exists in the United States today.”2 I believe that Pound’s words apply with at least equal force today as they did in 1906.
The United States has promoted the notion of the rule of law as a means for helping to ensure peace and democracy around the world. In our work with emerging nations and with the breakup of the Soviet Union, we have continual ly advocated the importance of the rule of law. One necessary component to achieving the rule of law, of course, is a fair, impartial, and independent judiciary. The United States ‘s federal judiciary has been the envy of the world for many
“The Threat to Judicial Independence”
In November, South Dakotans will vote on a state constitutional amendment being advocated by a national group called “JAIL 4 Judges.” If the amendment passes, it would eliminate judicial immunity, and enable a special grand jury to censure judges for their official legal determinations. Although the amendment’s supporters claim they seek a “judicial accountability initiative law” (JAIL), they aspire to something far more sinister — judicial intimidation. Indeed, the national Web site of JAIL 4 Judges boasts with striking candor that the organization “has that intimidation factor flowing through the judicial system.”
It is tempting to dismiss this proposed amendment as merely an isolated bout of anti-judge angst. But while the JAIL 4 Judges initiative is unusually venomous, it is far from alone in expressing skepticism of the judiciary. In addition to South Dakota, this election cycle has witnessed efforts in at least three other states that are designed to rein in judges who have supposedly “run amok.”
Not to be completely outdone, Congress also has engaged in recent efforts to police the judiciary. Seeking to constrain the legal sources that are available to judges, some members of Congress have advocated measures that would forbid judges from citing foreign law when they are interpreting the Constitution. In addition, bills have been introduced in both houses of Congress supporting the creation of an inspector general to investigate and monitor the federal bench. Finally,
Speech on judicial independence at Georgetown University
Sandra Day O’Connor I’m going to get you on my next book tour if I ever have one. That’s fun. And thank you my wonderful former colleagues for showing up today. Justice Thomas Justice Souter, and I think Justice Alito is going to join us if he’s not already here. And thank every one of you for coming and participating in this conference. I think you’ve already heard from President to Julia, and Michael trainer, why we’re doing this.
And it’s already been mentioned that 100 years ago this year, Roscoe pound, who went on to become dean of the Harvard Law School, gave his well publicized address to the American Bar, call the causes of popular dissatisfaction with the administration of justice. And he warned in that speech that we must not be deceived into overlooking or underwriting the real and serious dissatisfaction with courts and lack of respect for the law, which exists in the United States today. And I think that statement holds true today as well. We have promoted in this country, the notion of the rule of law as a means for helping ensure peace around the world, in our work with the emerging nations with the breakup of the Soviet Union, and in other countries we have actively urged upon every nation that we be concerned with the rule of law and The key component to that is a fair, impartial and independent judiciary. For a long time, I think the federal judiciary in this country has certainly been noted in other countries and admired and many would want to copy it. I
Interview on “Hardball with Chris Matthews”
Remarks on the release of the Iraq Study Group Report
Sandra Day O’Connor I would be willing to add a comment about what Leon Panetta has just expressed so well. We’ve said in the report that we agree with the goal of U.S. policy in Iraq, as stated by the president: an Iraq that can govern itself, sustain itself and defend itself. And to do that, we’ve made these various recommendations on a consensus basis.
It’s my belief that if a large segment of our country gets behind that, on a consensus basis, that it’s very likely we can move forward and make some progress toward that statement of goals.
And this is not an ongoing commission. It really is out of our hands, having done what we did. It’s up to you, frankly. You are the people who speak to the American people. You’re there interpreting this and talking to America. And I hope that the American people will feel that if they are behind something in broad terms, that we’ll be better off. I think we will, and I hope, in general, others think so, too.
Interview with Arizona Capitol Television
Unknown Speaker Thank you for joining us today I’m just honored to be sitting across from you interviewing you and to have you here with us. Sandra Day O’Connor You’re welcome. And I’m glad to be here. Unknown Speaker Most people already know that you paved the way for women by being the first woman on point to the US Supreme Court. But I think fewer people know that you also pave the way in Arizona by being the first woman, majority leader in any state senate. Right. In fact, there Sandra Day O’Connor there had been no woman, legislative leader in any post in across the country. And it was such a surprise to me when my colleagues voted in a closed ballot to select me as the majority leader. I was shocked. But it was a wonderful experience. I learned a lot. Unknown Speaker What would you say were some of the challenges that might have came along Sandra Day O’Connor with? Well, the challenges in those days was that it’s a small state Senate, they’re 32 members. And I was a Republican, and the republicans held a majority of one. So it was very challenging to work with that very narrow majority in the Republican Party. And what it meant was that for many pieces of legislation, in order to pass anything, we had to have support from the other side of the aisle. Luckily, it was a time in Arizona, when I don’t think the political feelings were as partisan as they seem to be at times today. And there were many says, When legislators from both parties would work together on legislation
Speech at 400th anniversary celebration of Jamestown, Virginia
Sandra Day O’Connor Thank you, Governor Page. Thank you. Thank you. Sandra Day O’Connor This is a great occasion. The volunteers, some 2000 of them, have been working for more than two years to make this weekend the incredible event that it is. And they’ve done a great job. We celebrate Jamestown’s 400th anniversary because that very difficult settlement gave us our start in representative democracy. It caused us to be an English-speaking nation. It brought to the shores our first venture capitalists, they came to try to make money. And I guess you could call it the start of a global economy. And most important to me, those settlers brought with them the rule of law, they brought the common law of Great Britain. That’s what the charter told them to bring with them. And they did. And that has lasted. And we are so grateful. And it is such an honor for this celebration, to have a visit today from the President of the United States and Mrs. Bush. This is truly special. When the planners started their plans, they said in our wildest dreams, we hope we will have the Queen of England return. And we hope the President and Mrs. Bush will come. And lo and behold, they’re here. And it is my enormous honor to present to you, the President of the United States.
Interview with Fox News Sunday
WASHINGTON – “FOX NEWS SUNDAY” HOST CHRIS WALLACE: Even though Sandra Day O’Connor has retired from the Supreme Court, that doesn’t mean the nation’s first female justice is taking it easy.
She’s in the process of putting together her own Web site to teach students about the court system and to try to answer critics she believes are going too far. We sat down with her late this week at the Supreme Court.
(BEGIN VIDEOTAPE)
Justice O’Connor, welcome to “FOX News Sunday.”
FORMER JUSTICE SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR: Thank you.
WALLACE: You say that one of the things that got you started thinking about this Web site were all of the partisan attacks on judges, all the talk about activist judges legislating from the court.
Why does that kind of talk disturb you?
O’CONNOR: It was a concern to me because I’ve lived a long time now. I’m a product of the last century, you know. And I do not remember a time when there were such a broad and widespread range of critics of judges.
Now, when I was a youngster I do remember seeing on the highway out by the Lazy B Ranch a big billboard saying, “Impeach Earl Warren,” and that was in the years when there were some cases like Miranda and some criminal cases, and people got all excited.
But what we’re seeing now is a more broadly based range of criticisms of the nation’s courts, both state and federal, and we saw it in the last election.
Do you remember in South Dakota there was a proposal on their ballot to amend the state constitution? It was
Speech on judicial independence to the National Governors Association
Unknown Speaker So Connor, Sandra Day O’Connor don’t do that. Thank you very much. Governor Napolitano is doing an outstanding job in my home state. And I was so appreciative when, as chairman of this group, she agreed that I could have a few words with you this morning. And that Tom Phillips, the former Chief Justice of the Texas Supreme Court, could also be part of this package and we hope to be brief and our remarks so that we might spend some time answering questions if there are some and Governor Granholm you’re a great hostess. I had not previously been to the Northern part of Michigan and it’s beautiful. It’s been such a treat to glimpse Traverse City and the surroundings. I just, it’s so enchanting, I hope to come back. Now, it’s Elementary, high school civics that we have three branches of government, not just governors and not just legislators. And they regulate each other by a very intricate system of checks and balances. And the main check the judicial branch has on the others is the power to declare statutes or executive acts unconstitutional. Although sometimes judges might check the political branches in a softer way merely by interpreting a statute in light of constitutional values, or by ruling that a regulation or executive act is not authorized by statute, but whatever courts do, the courts have the power to make The president or Congress, or a governor or a state legislature, really, really angry. In fact, if judges do not make the man some of the time,
“Civics and Citizens”
A survey conducted by the National Constitution Center recently revealed that fewer American teenagers could identify the three branches of government than could identify the Three Stooges.
While I enjoy Larry, Moe and Curly as much as anyone, there is nothing amusing about such statistics, because they reveal an absence of even the most basic knowledge about our governmental structure. Unless we do something to arrest this disturbing trend, I fear that the joke will be on all of us.
This trend is disturbing, because only an educated citizenry can ensure that our Nation’s commitment to liberty is upheld and the promise of Constitution fulfilled. A thorough civic education creates citizens who have a strong grasp of the fundamental processes of American democracy, an understanding of community issues and the ability to discuss those issues with one another and with leaders of the community.
The Framers of the United States Constitution understood the document that they created to be predicated on the involvement of educated citizens. If we fail to educate young people to become active and informed participants in our democracy, there is no question that our democracy will suffer. Such a failure would betray the trust bestowed upon us by the Constitution’s Framers.
The problem of civic illiteracy, as I have come to call it, is a relatively new phenomenon. Unlike some of the issues that ail society, however, the root cause of civic illiteracy is far from mysterious: We simply
The Importance of an Independent Judiciary
Stewart Schwab Good afternoon. Thank you for joining us today for Cornell University’s second annual Milton Konvitz Memorial Lecture. I’m Stewart Schwab, the Allan R. Tessler Dean of Cornell law school. And I have the distinct honor to serve as your moderator for this unique and special occasion. thanks to the generosity of Dr. Irwin Jacobs, who received his engineering degree here in 1954. And this is Joan Jacobs, who received her degree also in 1954. From Human Ecology, the Milton our convicts, visiting lectureship and American ideals honors the spirit of Professor Milton our convicts, and especially his theoretically rich and diverse American ideals course. The purpose of their gift is to bring a prominent expert in American democratic thought, ethics or political philosophy to campus to speak to the Cornell community. Both the law school and the IR school are proud to count Professor Milton comets as a former prominent faculty member. Professor conference was a founding member of the ILR school and also held a joint appointment and was a vital member of the law school faculty. But Professor conferences legendary reputation at Cornell stems in significant part from the fact that more than 8000 students university wide were students in his American ideals course from 1946 to 1973. In this course, undergraduates examine the writings and teachings of the great intellectual thinkers and philosophy Throughout history and throughout the world, who shaped American democratic values?
Keynote address at “The Presidency and the Supreme Court” conference
Thank you. Thank you very much. That was a wonderful introduction. You even found things I didn’t know. What is this nixon tape business? I have to find out about that.
Sandra Day O’Connor yeah. I’m going to have to find out more about that. Now, I’m so glad to be at hyde park. It is my first visit to this place. And I know part of the wallace family, and I think david douglas is sitting right there. And they helped make this facility possible, chi think is marvelous. I’m so glad to see that. Tomorrow I look forward to seeing the other parts of hyde park in the daylight hours. And my parents were cattle ranchers, as you have heard. Many of the cattle ranchers, at least in the southwest did not approve of franklin roosevelt’s policies at all. Quite the contrary. They didn’t approve of eleanor roosevelt either. I’m not sure why, but they didn’t. And when I was a child, we didn’t have a a school near the ranch, and I was sent off to el paso texas where I lived with a grandmother to go to school. And went to this school for girls. The head mistress, dr. Lucinda temp lynn invited ell minor roosevelt to come to the school, and eleanor roosevelt accepted. And all of us were supposed to clean up and be out by the flag pole, waiting for eleanor roosevelt to arrive. Ki remember to this day all of us being out there waiting and here — I did not dare tell my parents. [laughter] and of course I realized I couldn’t possibly like her. And so we all stood out by the flag pole, and the black
Balancing Security, Democracy, and Human Rights in an Age of Terrorism
Balancing Security, Democracy, and Human Rights in an Age of Terrorism
SANDRA DAY O’CONNOR*
This speech was presented by Sandra Day O’Connor upon receiving the Fall 2007 Wolfgang Friedmann Award for Outstanding Contributions to the Field of International Law in conjunction with the Harold Leventhal Memorial Lecture Series on November 12, 2007.
I would like to open my remarks tonight by describing a conflict between the executive and judicial branches of the United States government. Not long after the outbreak of war, the President of the United States altered the traditional understanding of civil liberties by finding that standard jury trials were incapable of meeting the necessities of wartime. In an effort to remedy this situation, the executive determined that some defendants should be tried by special military courts rather than traditional juries. The United States Supreme Court rejected that claim and found that the military courts lacked jurisdiction over those defendants who were U.S. citizens.
Now, this conflict sounds like it came directly from the New York Times or the Washington Post.But instead of describing President George W. Bush and the War on Terror of today, I am describing President Abraham Lincoln and our Civil War of the 1860s. President Lincoln decided that wartime needs required him to suspend our constitutional right to a writ of habeas corpus. In Ex parte Milligan,our Supreme Court held that military tribunals did not have jurisdiction over civilians
“Justice for Sale”
Voters generally don’t express much interest in the election of judges. This year, as in years past, voter turnout in elections for judges was very low. But judicial elections, which occur in some form in 39 states, are receiving growing attention from those who seek to influence them. In fact, motivated interest groups are pouring money into judicial elections in record amounts. Whether or not they succeed in their attempts to sway the voters, these efforts threaten the integrity of judicial selection and compromise public perception of judicial decisions.
The final four candidates running for open seats on the Supreme Court of Pennsylvania raised more than $5.4 million combined in 2007, shattering fund-raising records in Pennsylvania judicial elections. Since 2006, high court campaigns in Georgia, Kentucky, Oregon and Washington also set fund-raising records. Since 2004, nine other states broke records for high court election spending.
Most of this money comes from special interest groups who believe that their contributions can help elect judges likely to rule in a manner favorable to their causes. As interest-group spending rises, public confidence in the judiciary declines. Nine out of 10 Pennsylvanians regard judicial fund raising as evidence that justice is for sale, and many judges agree. According to a nationwide survey by the Annenberg Public Policy Institute, partisan judicial elections decrease public confidence that courts are fair, impartial and operating in
Interview with Scholastic News
Sandra Day O’Connor greets Kid Reporter Danny Murphy in the Lawyers’ Lounge in the Supreme Court Building. (Photo: Ron Sachs/Consolidated News Photos)
September 17 is Constitution Day. On Constitution Day, we honor and celebrate the cornerstone of our government. The Constitution is the most important document in the United States. It’s the basis of our government and provides us with our rights. On this Constitution Day, Scholastic News talks with constitutional expert and the first female Supreme Court Justice, Sandra Day O’Connor. As a Supreme Court Justice from 1981 through 2006, O’Connor decided with laws or decisions made by other courts were constitutional. Sometimes, laws are passed or decisions are made that some people think violate the Constitution. When that happens, cases are brought before the nine members of the Supreme Court. This process is called “checks and balances,” and is an important part of the Constitution. Once you’ve read the interview with Sandra Day O’Connor, read more about the Constitution and the views of other constitutional experts and play the Constitution Game in the Constitution Day Special Report!
Scholastic News: What was your favorite subject in school?
Sandra Day O’Connor: That’s so hard to say. It’s been such a long time since I was in school. I think probably history. What’s your favorite subject?
SN: History also.
O’Connor: How about that! Except I went to school in El Paso, Texas, and every single year I was there from kindergarten
Reflections on Arizona’s Judicial Selection Process
REFLECTIONS ON ARIZONA’S JUDICIAL SELECTION PROCESS
Sandra Day O’Connor* & RonNell Andersen Jones**
Using Arizona as a case study, this Essay examines the history of changes in state judicial-selection rationales, methods, and practices. It outlines Arizona’s journey from contested elections to a hybrid merit-selection system featuring appointments and retention elections, and compares this experience to that of states that have continued with a pure election system. The Essay explores the purported tension between judicial accountability and judicial independence and argues that Arizona’s experience demonstrates both the falsity of that dichotomy and the superiority of a hybrid merit-selection system in simultaneously promoting accountability, independence, competency, and fairness.
INTRODUCTION
This 50th Anniversary Issue of the Arizona Law Review presents a wonderful opportunity to look back at some remarkable legal developments of the latter half of the twentieth century and the issues that have impacted the work of the judicial branch during that time. One important development is a shift in the issues surrounding the judicial selection process. This trend is particularly notable at the state level because selection processes in the states are easier to change, interest has historically been much lower, and more litigation takes place at the state level than in the federal judicial system.1 Judicial selection methods and the practices surrounding them have a great impact
Judicial Accountability Must Safeguard, Not Threaten, Judicial Independence: An Introduction
This issue of the Denver University Law Review is devoted to an important subject: judicial accountability. Properly understood, judicial accountability is a fundamental democratic requirement of our federal and State governments. Put simply, judges must be accountable to the public for their constitutional role of applying the law fairly and impartially. Judicial accountability, however, is a concept that is frequently misunderstood at best and abused at worst. It has become a rallying cry for those who want in reality to dictate substantive judicial outcomes. The notion of accountability is superficially attractive: judges who reach outcomes that part ways with the will of the majority—often mislabeled “activist” judges—should be held “accountable.”
This simplistic understanding of accountability—judicial accountability for the majority’s desired substantive outcomes—ignores the role of the judiciary and indeed the very structure of our democratic governments, State and federal. Worse, this perversion of the concept of judicial accountability threatens to undermine the safeguards of democracy and liberty that were so brilliantly conceived by those who first designed our governmental institutions and drafted our Constitution. In short, “[p]opulist, substance-based accountability for judges is precisely what the Founders feared[.]”1 The Framers placed at the core of the judiciary’s design the concept of judicial independence as a means to guarantee the Rule of Law. Judicial
“How to Save Our Courts”
In my work as a Supreme Court justice, I was required by the Constitution to fairly and impartially apply the law—not the law as I wanted it to be but the law as it was. Now, as a private citizen, I am anxious about the state of the judiciary in America. I am not concerned about particular judges or cases, nor am I concerned about the judiciary shifting right or left.What worries me is the manner in which politically motivated interest groups are attempting to interfere with justice. The rule of law in the U.S. includes statutes and constitutional provisions. It also involves precedent, which is a previous judicial ruling on a matter. A judge typically defers to precedent. Like good cooking, good judging requires taking ingredients and procedures used successfully in the past and adjusting them to the case at hand. New legal recipes—or rules—can have major ramifications. So if a judge comes up with a new way to apply the law, her opinion may be reviewed by state or federal appellate courts to ensure that it is a correct interpretation of the law. If it’s not, it’s overturned. Thus, our judicial system has safeguards to ensure consistency and preservation of the law. But it is threatened when judges ignore settled law and make decisions according to personal or public preferences. The judiciary currently is experiencing unprecedented pressure from interest groups to make decisions that are based on politics. In Washington, D.C., we hear a lot about federal judges, and they have
Commencement address at Gettysburg College
It is a great pleasure to be with you today at Gettysburg College. After all, it is a day of joy for everyone: you graduates have no more university exams or class to endure. And I might say, the faculty no longer has you to endure; you have fame and fortune ahead of you; your families and spouses and friends can look forward to seeing more of you; and your speaker has a respite from her labors across the nation.
I realize we have gathered here today to applaud those of you who will be receiving degrees. I suggest, however, that there are several heroes and heroines here today who should be recognized and with whom you graduates would like to share your glory. I refer, of course, to the parents, who have made two significant contributions to your presence today. First, they had the brains, which you were lucky enough to inherit, and, secondly, they probably provided at least some of the money you needed to sustain yourselves while you were here. I congratulate your parents, and I commend you graduates for your good judgment in selecting them.
A commencement speech is a particularly difficult assignment. The speaker is given no topic and is expected to be able to inspire all the graduates with a stirring speech about nothing at al. I suppose that’s why so many lawyers are asked to be commencement speakers: they’re in the habit of talking extensively even when they have nothing to say.
In this case the College asked not only a lawyer but an elderly judge to be the commencement